Help us make food transparency the norm!
As a non-profit organization, we depend on your donations to continue informing consumers around the world about what they eat.
The food revolution starts with you!
Bear claw danish - Cloverhill
Bear claw danish - Cloverhill
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barcode: 0085264316401 (EAN / EAN-13) 085264316401 (UPC / UPC-A)
Brands: Cloverhill
Brand owner: Aryzta, LLC
Categories: Snacks, Sweet snacks, Biscuits and cakes, Cakes
Countries where sold: United States
Matching with your preferences
Health
Ingredients
-
66 ingredients
enriched flour (wheat flour, malted barley flour, niacin, ferrous sulfate or reduced iron, thiamine mononitrate, riboflavin, folic acid), water, sugar, palm oil, contains 2% or less: yeast, cream cheese (cultured cream and milk), cornstarch, whey, mono and diglycerides, salt, corn syrup, egg white, modified cornstarch, natural and artificial flavor, cherry, dextrose, calcium carbonate, soybean oil, cellulose gum, guar gum, mineral oil, sodium stearoyl lactylate, citric acid, sodium citrate, soy lecithin, calcium sulfate, calcium caseinate, lactose, ascorbic acid, egg, maltodextrin, baking soda, sodium acid pyrophosphate, agar, preservative (calcium propionate, potassium sorbate, sodium propionate, sodium benzoate, sorbic acid), fumaric acid, enzymes, sodium hexametaphosphate, lactic acid, color (beta carotene, titanium dioxide, red 40, blue 1), carrageenan, pectin, locust bean gum, sodium phosphate, xanthan gum, vitamin a palmitateAllergens: Eggs, Gluten, Milk, Soybeans
Food processing
-
Ultra processed foods
Elements that indicate the product is in the 4 - Ultra processed food and drink products group:
- Additive: E129 - Allura red
- Additive: E133 - Brilliant blue FCF
- Additive: E160a - Carotene
- Additive: E171 - Titanium dioxide
- Additive: E322 - Lecithins
- Additive: E406 - Agar
- Additive: E407 - Carrageenan
- Additive: E410 - Locust bean gum
- Additive: E412 - Guar gum
- Additive: E415 - Xanthan gum
- Additive: E440 - Pectins
- Additive: E450 - Diphosphates
- Additive: E452 - Polyphosphates
- Additive: E466 - Sodium carboxy methyl cellulose
- Additive: E471 - Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids
- Additive: E481 - Sodium stearoyl-2-lactylate
- Additive: E905 - Synthetic wax
- Ingredient: Colour
- Ingredient: Dextrose
- Ingredient: Flavouring
- Ingredient: Glucose
- Ingredient: Lactose
- Ingredient: Maltodextrin
- Ingredient: Whey
Food products are classified into 4 groups according to their degree of processing:
- Unprocessed or minimally processed foods
- Processed culinary ingredients
- Processed foods
- Ultra processed foods
The determination of the group is based on the category of the product and on the ingredients it contains.
Additives
-
E129 - Allura red
Allura Red AC: Allura Red AC is a red azo dye that goes by several names, including FD&C Red 40. It is used as a food dye and has the E number E129. It is usually supplied as its red sodium salt, but can also be used as the calcium and potassium salts. These salts are soluble in water. In solution, its maximum absorbance lies at about 504 nm.Source: Wikipedia
-
E133 - Brilliant blue FCF
Brilliant Blue FCF: Brilliant Blue FCF -Blue 1- is an organic compound classified as a triarylmethane dye and a blue azo dye, reflecting its chemical structure. Known under various commercial names, it is a colorant for foods and other substances. It is denoted by E number E133 and has a color index of 42090. It has the appearance of a blue powder. It is soluble in water, and the solution has a maximum absorption at about 628 nanometers.Source: Wikipedia
-
E160a - Carotene
Carotene: The term carotene -also carotin, from the Latin carota, "carrot"- is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals -with the exception of some aphids and spider mites which acquired the synthesizing genes from fungi-. Carotenes are photosynthetic pigments important for photosynthesis. Carotenes contain no oxygen atoms. They absorb ultraviolet, violet, and blue light and scatter orange or red light, and -in low concentrations- yellow light. Carotenes are responsible for the orange colour of the carrot, for which this class of chemicals is named, and for the colours of many other fruits, vegetables and fungi -for example, sweet potatoes, chanterelle and orange cantaloupe melon-. Carotenes are also responsible for the orange -but not all of the yellow- colours in dry foliage. They also -in lower concentrations- impart the yellow coloration to milk-fat and butter. Omnivorous animal species which are relatively poor converters of coloured dietary carotenoids to colourless retinoids have yellowed-coloured body fat, as a result of the carotenoid retention from the vegetable portion of their diet. The typical yellow-coloured fat of humans and chickens is a result of fat storage of carotenes from their diets. Carotenes contribute to photosynthesis by transmitting the light energy they absorb to chlorophyll. They also protect plant tissues by helping to absorb the energy from singlet oxygen, an excited form of the oxygen molecule O2 which is formed during photosynthesis. β-Carotene is composed of two retinyl groups, and is broken down in the mucosa of the human small intestine by β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase to retinal, a form of vitamin A. β-Carotene can be stored in the liver and body fat and converted to retinal as needed, thus making it a form of vitamin A for humans and some other mammals. The carotenes α-carotene and γ-carotene, due to their single retinyl group -β-ionone ring-, also have some vitamin A activity -though less than β-carotene-, as does the xanthophyll carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin. All other carotenoids, including lycopene, have no beta-ring and thus no vitamin A activity -although they may have antioxidant activity and thus biological activity in other ways-. Animal species differ greatly in their ability to convert retinyl -beta-ionone- containing carotenoids to retinals. Carnivores in general are poor converters of dietary ionone-containing carotenoids. Pure carnivores such as ferrets lack β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase and cannot convert any carotenoids to retinals at all -resulting in carotenes not being a form of vitamin A for this species-; while cats can convert a trace of β-carotene to retinol, although the amount is totally insufficient for meeting their daily retinol needs.Source: Wikipedia
-
E160ai - Beta-carotene
Beta-Carotene: β-Carotene is an organic, strongly colored red-orange pigment abundant in plants and fruits. It is a member of the carotenes, which are terpenoids -isoprenoids-, synthesized biochemically from eight isoprene units and thus having 40 carbons. Among the carotenes, β-carotene is distinguished by having beta-rings at both ends of the molecule. β-Carotene is biosynthesized from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate.β-Carotene is the most common form of carotene in plants. When used as a food coloring, it has the E number E160a. The structure was deduced by Karrer et al. in 1930. In nature, β-carotene is a precursor -inactive form- to vitamin A via the action of beta-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase.Isolation of β-carotene from fruits abundant in carotenoids is commonly done using column chromatography. It can also be extracted from the beta-carotene rich algae, Dunaliella salina. The separation of β-carotene from the mixture of other carotenoids is based on the polarity of a compound. β-Carotene is a non-polar compound, so it is separated with a non-polar solvent such as hexane. Being highly conjugated, it is deeply colored, and as a hydrocarbon lacking functional groups, it is very lipophilic.Source: Wikipedia
-
E171 - Titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide: Titanium dioxide, also known as titaniumIV oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 -PW6-, or CI 77891. Generally, it is sourced from ilmenite, rutile and anatase. It has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million metric tons. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and the oxide has been valued at $13.2 billion.Source: Wikipedia
-
E200 - Sorbic acid
Sorbic acid: Sorbic acid, or 2‚4-hexadienoic acid, is a natural organic compound used as a food preservative. It has the chemical formula CH3-CH-4CO2H. It is a colourless solid that is slightly soluble in water and sublimes readily. It was first isolated from the unripe berries of the Sorbus aucuparia -rowan tree-, hence its name.Source: Wikipedia
-
E202 - Potassium sorbate
Potassium sorbate (E202) is a synthetic food preservative commonly used to extend the shelf life of various food products.
It works by inhibiting the growth of molds, yeast, and some bacteria, preventing spoilage. When added to foods, it helps maintain their freshness and quality.
Some studies have shown that when combined with nitrites, potassium sorbate have genotoxic activity in vitro. However, potassium sorbate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory authorities.
-
E211 - Sodium benzoate
Sodium benzoate: Sodium benzoate is a substance which has the chemical formula NaC7H5O2. It is a widely used food preservative, with an E number of E211. It is the sodium salt of benzoic acid and exists in this form when dissolved in water. It can be produced by reacting sodium hydroxide with benzoic acid.Source: Wikipedia
-
E270 - Lactic acid
Lactic acid: Lactic acid is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH-OH-COOH. In its solid state, it is white and water-soluble. In its liquid state, it is colorless. It is produced both naturally and synthetically. With a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group, lactic acid is classified as an alpha-hydroxy acid -AHA-. In the form of its conjugate base called lactate, it plays a role in several biochemical processes. In solution, it can ionize a proton from the carboxyl group, producing the lactate ion CH3CH-OH-CO−2. Compared to acetic acid, its pKa is 1 unit less, meaning lactic acid deprotonates ten times more easily than acetic acid does. This higher acidity is the consequence of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the α-hydroxyl and the carboxylate group. Lactic acid is chiral, consisting of two optical isomers. One is known as L--+--lactic acid or -S--lactic acid and the other, its mirror image, is D--−--lactic acid or -R--lactic acid. A mixture of the two in equal amounts is called DL-lactic acid, or racemic lactic acid. Lactic acid is hygroscopic. DL-lactic acid is miscible with water and with ethanol above its melting point which is around 17 or 18 °C. D-lactic acid and L-lactic acid have a higher melting point. In animals, L-lactate is constantly produced from pyruvate via the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase -LDH- in a process of fermentation during normal metabolism and exercise. It does not increase in concentration until the rate of lactate production exceeds the rate of lactate removal, which is governed by a number of factors, including monocarboxylate transporters, concentration and isoform of LDH, and oxidative capacity of tissues. The concentration of blood lactate is usually 1–2 mM at rest, but can rise to over 20 mM during intense exertion and as high as 25 mM afterward. In addition to other biological roles, L-lactic acid is the primary endogenous agonist of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1 -HCA1-, which is a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor -GPCR-.In industry, lactic acid fermentation is performed by lactic acid bacteria, which convert simple carbohydrates such as glucose, sucrose, or galactose to lactic acid. These bacteria can also grow in the mouth; the acid they produce is responsible for the tooth decay known as caries. In medicine, lactate is one of the main components of lactated Ringer's solution and Hartmann's solution. These intravenous fluids consist of sodium and potassium cations along with lactate and chloride anions in solution with distilled water, generally in concentrations isotonic with human blood. It is most commonly used for fluid resuscitation after blood loss due to trauma, surgery, or burns.Source: Wikipedia
-
E281 - Sodium propionate
Sodium propionate: Sodium propanoate or sodium propionate is the sodium salt of propionic acid which has the chemical formula Na-C2H5COO-. This white crystalline solid is deliquescent in moist air.Source: Wikipedia
-
E282 - Calcium propionate
Calcium propanoate: Calcium propanoate or calcium propionate has the formula Ca-C2H5COO-2. It is the calcium salt of propanoic acid.Source: Wikipedia
-
E297 - Fumaric acid
Fumaric acid: Fumaric acid or trans-butenedioic acid is the chemical compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. It is produced in eukaryotic organisms from succinate in complex 2 of the electron transport chain via the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase. It is one of two isomeric unsaturated dicarboxylic acids, the other being maleic acid. In fumaric acid the carboxylic acid groups are trans -E- and in maleic acid they are cis -Z-. Fumaric acid has a fruit-like taste. The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the C4H2O2−4 ion -in solution-.Source: Wikipedia
-
E322 - Lecithins
Lecithins are natural compounds commonly used in the food industry as emulsifiers and stabilizers.
Extracted from sources like soybeans and eggs, lecithins consist of phospholipids that enhance the mixing of oil and water, ensuring smooth textures in various products like chocolates, dressings, and baked goods.
They do not present any known health risks.
-
E322i - Lecithin
Lecithins are natural compounds commonly used in the food industry as emulsifiers and stabilizers.
Extracted from sources like soybeans and eggs, lecithins consist of phospholipids that enhance the mixing of oil and water, ensuring smooth textures in various products like chocolates, dressings, and baked goods.
They do not present any known health risks.
-
E330 - Citric acid
Citric acid is a natural organic acid found in citrus fruits such as lemons, oranges, and limes.
It is widely used in the food industry as a flavor enhancer, acidulant, and preservative due to its tart and refreshing taste.
Citric acid is safe for consumption when used in moderation and is considered a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) food additive by regulatory agencies worldwide.
-
E406 - Agar
Agar: Agar -pronounced , sometimes - or agar-agar is a jelly-like substance, obtained from red algae.Agar is a mixture of two components: the linear polysaccharide agarose, and a heterogeneous mixture of smaller molecules called agaropectin. It forms the supporting structure in the cell walls of certain species of algae, and is released on boiling. These algae are known as agarophytes, and belong to the Rhodophyta -red algae- phylum.Agar has been used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia, and also as a solid substrate to contain culture media for microbiological work. Agar can be used as a laxative, an appetite suppressant, a vegetarian substitute for gelatin, a thickener for soups, in fruit preserves, ice cream, and other desserts, as a clarifying agent in brewing, and for sizing paper and fabrics.The gelling agent in agar is an unbranched polysaccharide obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from tengusa -Gelidiaceae- and ogonori -Gracilaria-. For commercial purposes, it is derived primarily from ogonori. In chemical terms, agar is a polymer made up of subunits of the sugar galactose.Source: Wikipedia
-
E407 - Carrageenan
Carrageenan (E407), derived from red seaweed, is widely employed in the food industry as a gelling, thickening, and stabilizing agent, notably in dairy and meat products.
It can exist in various forms, each imparting distinct textural properties to food.
However, its degraded form, often referred to as poligeenan, has raised health concerns due to its potential inflammatory effects and its classification as a possible human carcinogen (Group 2B) by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).
Nevertheless, food-grade carrageenan has been deemed safe by various regulatory bodies when consumed in amounts typically found in food.
-
E410 - Locust bean gum
Locust bean gum: Locust bean gum -LBG, also known as carob gum, carob bean gum, carobin, E410- is a thickening agent and a gelling agent used in food technology.Source: Wikipedia
-
E412 - Guar gum
Guar gum (E412) is a natural food additive derived from guar beans.
This white, odorless powder is valued for its remarkable thickening and stabilizing properties, making it a common ingredient in various food products, including sauces, dressings, and ice creams.
When used in moderation, guar gum is considered safe for consumption, with no known adverse health effects.
-
E415 - Xanthan gum
Xanthan gum (E415) is a natural polysaccharide derived from fermented sugars, often used in the food industry as a thickening and stabilizing agent.
This versatile food additive enhances texture and prevents ingredient separation in a wide range of products, including salad dressings, sauces, and gluten-free baked goods.
It is considered safe for consumption even at high intake amounts.
-
E440 - Pectins
Pectins (E440) are natural carbohydrates, predominantly found in fruits, that act as gelling agents in the food industry, creating the desirable jelly-like texture in jams, jellies, and marmalades.
Pectins stabilize and thicken various food products, such as desserts, confectioneries, and beverages, ensuring a uniform consistency and quality.
Recognized as safe by various health authorities, pectins have been widely used without notable adverse effects when consumed in typical dietary amounts.
-
E450 - Diphosphates
Diphosphates (E450) are food additives often utilized to modify the texture of products, acting as leavening agents in baking and preventing the coagulation of canned food.
These salts can stabilize whipped cream and are also found in powdered products to maintain their flow properties. They are commonly present in baked goods, processed meats, and soft drinks.
Derived from phosphoric acid, they're part of our daily phosphate intake, which often surpasses recommended levels due to the prevalence of phosphates in processed foods and drinks.
Excessive phosphate consumption is linked to health issues, such as impaired kidney function and weakened bone health. Though diphosphates are generally regarded as safe when consumed within established acceptable daily intakes, it's imperative to monitor overall phosphate consumption to maintain optimal health.
-
E466 - Sodium carboxy methyl cellulose
Carboxymethyl cellulose: Carboxymethyl cellulose -CMC- or cellulose gum or tylose powder is a cellulose derivative with carboxymethyl groups --CH2-COOH- bound to some of the hydroxyl groups of the glucopyranose monomers that make up the cellulose backbone. It is often used as its sodium salt, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose.Source: Wikipedia
-
E471 - Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids
Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E471), are food additives commonly used as emulsifiers in various processed foods.
These compounds consist of glycerol molecules linked to one or two fatty acid chains, which help stabilize and blend water and oil-based ingredients. E471 enhances the texture and shelf life of products like margarine, baked goods, and ice cream, ensuring a smooth and consistent texture.
It is generally considered safe for consumption within established regulatory limits.
-
E481 - Sodium stearoyl-2-lactylate
Sodium stearoyl lactylate: Sodium stearoyl-2-lactylate -sodium stearoyl lactylate or SSL- is a versatile, FDA approved food additive used to improve the mix tolerance and volume of processed foods. It is one type of a commercially available lactylate. SSL is non-toxic, biodegradable, and typically manufactured using biorenewable feedstocks. Because SSL is a safe and highly effective food additive, it is used in a wide variety of products ranging from baked goods and desserts to pet foods.As described by the Food Chemicals Codex 7th edition, SSL is a cream-colored powder or brittle solid. SSL is currently manufactured by the esterification of stearic acid with lactic acid and partially neutralized with either food-grade soda ash -sodium carbonate- or caustic soda -concentrated sodium hydroxide-. Commercial grade SSL is a mixture of sodium salts of stearoyl lactylic acids and minor proportions of other sodium salts of related acids. The HLB for SSL is 10-12. SSL is slightly hygroscopic, soluble in ethanol and in hot oil or fat, and dispersible in warm water. These properties are the reason that SSL is an excellent emulsifier for fat-in-water emulsions and can also function as a humectant.Source: Wikipedia
-
E500 - Sodium carbonates
Sodium carbonates (E500) are compounds commonly used in food preparation as leavening agents, helping baked goods rise by releasing carbon dioxide when they interact with acids.
Often found in baking soda, they regulate the pH of food, preventing it from becoming too acidic or too alkaline. In the culinary world, sodium carbonates can also enhance the texture and structure of foods, such as noodles, by modifying the gluten network.
Generally recognized as safe, sodium carbonates are non-toxic when consumed in typical amounts found in food.
-
E500ii - Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Sodium hydrogen carbonate, also known as E500ii, is a food additive commonly used as a leavening agent.
When added to recipes, it releases carbon dioxide gas upon exposure to heat or acids, causing dough to rise and resulting in a light, fluffy texture in baked goods.
It is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory authorities when used in appropriate quantities and poses no significant health risks when consumed in typical food applications.
-
E905 - Synthetic wax
Microcrystalline wax: Microcrystalline waxes are a type of wax produced by de-oiling petrolatum, as part of the petroleum refining process. In contrast to the more familiar paraffin wax which contains mostly unbranched alkanes, microcrystalline wax contains a higher percentage of isoparaffinic -branched- hydrocarbons and naphthenic hydrocarbons. It is characterized by the fineness of its crystals in contrast to the larger crystal of paraffin wax. It consists of high molecular weight saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons. It is generally darker, more viscous, denser, tackier and more elastic than paraffin waxes, and has a higher molecular weight and melting point. The elastic and adhesive characteristics of microcrystalline waxes are related to the non-straight chain components which they contain. Typical microcrystalline wax crystal structure is small and thin, making them more flexible than paraffin wax. It is commonly used in cosmetic formulations. Microcrystalline waxes when produced by wax refiners are typically produced to meet a number of ASTM specifications. These include congeal point -ASTM D938-, needle penetration -D1321-, color -ASTM D6045-, and viscosity -ASTM D445-. Microcrystalline waxes can generally be put into two categories: "laminating" grades and "hardening" grades. The laminating grades typically have a melt point of 140-175 F -60 - 80 oC- and needle penetration of 25 or above. The hardening grades will range from about 175-200 F -80 - 93 oC-, and have a needle penetration of 25 or below. Color in both grades can range from brown to white, depending on the degree of processing done at the refinery level. Microcrystalline waxes are derived from the refining of the heavy distillates from lubricant oil production. This by-product must then be de-oiled at a wax refinery. Depending on the end use and desired specification, the product may then have its odor removed and color removed -which typically starts as a brown or dark yellow-. This is usually done by means of a filtration method or by hydro-treating the wax material.Source: Wikipedia
-
E905a - Mineral oil
Microcrystalline wax: Microcrystalline waxes are a type of wax produced by de-oiling petrolatum, as part of the petroleum refining process. In contrast to the more familiar paraffin wax which contains mostly unbranched alkanes, microcrystalline wax contains a higher percentage of isoparaffinic -branched- hydrocarbons and naphthenic hydrocarbons. It is characterized by the fineness of its crystals in contrast to the larger crystal of paraffin wax. It consists of high molecular weight saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons. It is generally darker, more viscous, denser, tackier and more elastic than paraffin waxes, and has a higher molecular weight and melting point. The elastic and adhesive characteristics of microcrystalline waxes are related to the non-straight chain components which they contain. Typical microcrystalline wax crystal structure is small and thin, making them more flexible than paraffin wax. It is commonly used in cosmetic formulations. Microcrystalline waxes when produced by wax refiners are typically produced to meet a number of ASTM specifications. These include congeal point -ASTM D938-, needle penetration -D1321-, color -ASTM D6045-, and viscosity -ASTM D445-. Microcrystalline waxes can generally be put into two categories: "laminating" grades and "hardening" grades. The laminating grades typically have a melt point of 140-175 F -60 - 80 oC- and needle penetration of 25 or above. The hardening grades will range from about 175-200 F -80 - 93 oC-, and have a needle penetration of 25 or below. Color in both grades can range from brown to white, depending on the degree of processing done at the refinery level. Microcrystalline waxes are derived from the refining of the heavy distillates from lubricant oil production. This by-product must then be de-oiled at a wax refinery. Depending on the end use and desired specification, the product may then have its odor removed and color removed -which typically starts as a brown or dark yellow-. This is usually done by means of a filtration method or by hydro-treating the wax material.Source: Wikipedia
Ingredients analysis
-
Palm oil
Ingredients that contain palm oil: Palm oil
-
Non-vegan
Non-vegan ingredients: Cream cheese, Sour cream, Milk, Whey, Egg white, Calcium caseinate, Lactose, EggSome ingredients could not be recognized.
We need your help!
You can help us recognize more ingredients and better analyze the list of ingredients for this product and others:
- Edit this product page to correct spelling mistakes in the ingredients list, and/or to remove ingredients in other languages and sentences that are not related to the ingredients.
- Add new entries, synonyms or translations to our multilingual lists of ingredients, ingredient processing methods, and labels.
If you would like to help, join the #ingredients channel on our Slack discussion space and/or learn about ingredients analysis on our wiki. Thank you!
-
Vegetarian status unknown
Unrecognized ingredients: Ferrous sulfate, Reduced iron, Thiamin mononitrate, Folic acid, Contains-2-and-less, Sodium citrateSome ingredients could not be recognized.
We need your help!
You can help us recognize more ingredients and better analyze the list of ingredients for this product and others:
- Edit this product page to correct spelling mistakes in the ingredients list, and/or to remove ingredients in other languages and sentences that are not related to the ingredients.
- Add new entries, synonyms or translations to our multilingual lists of ingredients, ingredient processing methods, and labels.
If you would like to help, join the #ingredients channel on our Slack discussion space and/or learn about ingredients analysis on our wiki. Thank you!
-
Details of the analysis of the ingredients
We need your help!
Some ingredients could not be recognized.
We need your help!
You can help us recognize more ingredients and better analyze the list of ingredients for this product and others:
- Edit this product page to correct spelling mistakes in the ingredients list, and/or to remove ingredients in other languages and sentences that are not related to the ingredients.
- Add new entries, synonyms or translations to our multilingual lists of ingredients, ingredient processing methods, and labels.
If you would like to help, join the #ingredients channel on our Slack discussion space and/or learn about ingredients analysis on our wiki. Thank you!
: flour (wheat flour, malted barley flour, niacin, ferrous sulfate, reduced iron, thiamine mononitrate, riboflavin, folic acid), water, sugar, palm oil, contains 2% and less (yeast), cream cheese (cultured cream, milk), cornstarch, whey, mono- and diglycerides, salt, corn syrup, egg white, modified cornstarch, natural and artificial flavor, cherry, dextrose, calcium carbonate, soybean oil, cellulose gum, guar gum, mineral oil, sodium stearoyl lactylate, citric acid, sodium citrate, soy lecithin, calcium sulfate, calcium caseinate, lactose, ascorbic acid, egg, maltodextrin, baking soda, sodium acid pyrophosphate, agar, preservative (calcium propionate, potassium sorbate, sodium propionate, sodium benzoate, sorbic acid), fumaric acid, enzymes, sodium hexametaphosphate, lactic acid, color (beta carotene, titanium dioxide, red 40, blue 1), carrageenan, pectin, locust bean gum, sodium phosphate, xanthan gum, vitamin a palmitate- flour -> en:flour - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9410 - percent_min: 2.17391304347826 - percent_max: 100
- wheat flour -> en:wheat-flour - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9410 - percent_min: 0.271739130434783 - percent_max: 100
- malted barley flour -> en:barley-malt-flour - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 9550 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 50
- niacin -> en:e375 - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 33.3333333333333
- ferrous sulfate -> en:ferrous-sulfate - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 25
- reduced iron -> en:reduced-iron - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 20
- thiamine mononitrate -> en:thiamin-mononitrate - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 16.6666666666667
- riboflavin -> en:e101 - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 14.2857142857143
- folic acid -> en:folic-acid - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 12.5
- water -> en:water - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 18066 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 50
- sugar -> en:sugar - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 31016 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 26.666666666667
- palm oil -> en:palm-oil - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - from_palm_oil: yes - ciqual_food_code: 16129 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 25
- contains 2% and less -> en:contains-2-and-less - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 20
- yeast -> en:yeast - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 20
- cream cheese -> en:cream-cheese - vegan: no - vegetarian: maybe - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 12999 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 16.6666666666667
- cultured cream -> en:sour-cream - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 19402 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 16.6666666666667
- milk -> en:milk - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 19051 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 8.33333333333333
- cornstarch -> en:corn-starch - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 9510 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 14.2857142857143
- whey -> en:whey - vegan: no - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 12.5
- mono- and diglycerides -> en:e471 - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - from_palm_oil: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 11.1111111111111
- salt -> en:salt - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 11058 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- corn syrup -> en:corn-syrup - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 31089 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- egg white -> en:egg-white - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 22001 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- modified cornstarch -> en:modified-corn-starch - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 9510 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- natural and artificial flavor -> en:natural-and-artificial-flavouring - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- cherry -> en:cherry - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13008 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- dextrose -> en:dextrose - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 31016 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- calcium carbonate -> en:e170i - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- soybean oil -> en:soya-oil - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - from_palm_oil: no - ciqual_food_code: 17420 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- cellulose gum -> en:e466 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- guar gum -> en:e412 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- mineral oil -> en:e905a - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- sodium stearoyl lactylate -> en:e481 - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - from_palm_oil: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- citric acid -> en:e330 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- sodium citrate -> en:sodium-citrate - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- soy lecithin -> en:soya-lecithin - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 42200 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- calcium sulfate -> en:e516 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- calcium caseinate -> en:calcium-caseinate - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- lactose -> en:lactose - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- ascorbic acid -> en:e300 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- egg -> en:egg - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 22000 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- maltodextrin -> en:maltodextrin - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- baking soda -> en:e500ii - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- sodium acid pyrophosphate -> en:e450i - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- agar -> en:e406 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 11084 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- preservative -> en:preservative - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- calcium propionate -> en:e282 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- potassium sorbate -> en:e202 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.54166666666665
- sodium propionate -> en:e281 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.3611111111111
- sodium benzoate -> en:e211 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.270833333333325
- sorbic acid -> en:e200 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.21666666666666
- fumaric acid -> en:e297 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- enzymes -> en:enzyme - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- sodium hexametaphosphate -> en:e452i - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- lactic acid -> en:e270 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- color -> en:colour - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- beta carotene -> en:e160ai - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - from_palm_oil: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- titanium dioxide -> en:e171 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.54166666666665
- red 40 -> en:e129 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.3611111111111
- blue 1 -> en:e133 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.270833333333325
- carrageenan -> en:e407 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- pectin -> en:e440a - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- locust bean gum -> en:e410 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- sodium phosphate -> en:e339 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- xanthan gum -> en:e415 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
- vitamin a palmitate -> en:retinyl-palmitate - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.0833333333333
Nutrition
-
Bad nutritional quality
⚠ ️Warning: the amount of fruits, vegetables and nuts is not specified on the label, it was estimated from the list of ingredients: 0This product is not considered a beverage for the calculation of the Nutri-Score.
Positive points: 0
- Proteins: 3 / 5 (value: 5, rounded value: 5)
- Fiber: 0 / 5 (value: 0.83333333333333, rounded value: 0.83)
- Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and colza/walnut/olive oils: 0 / 5 (value: 0.00298541525135931, rounded value: 0)
Negative points: 20
- Energy: 4 / 10 (value: 1536, rounded value: 1536)
- Sugars: 5 / 10 (value: 26.666666666667, rounded value: 26.67)
- Saturated fat: 7 / 10 (value: 7.5, rounded value: 7.5)
- Sodium: 4 / 10 (value: 433.33333333332, rounded value: 433.3)
The points for proteins are not counted because the negative points are greater or equal to 11.
Nutritional score: (20 - 0)
Nutri-Score:
-
Nutrient levels
-
Fat in moderate quantity (14.2%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Saturated fat in high quantity (7.5%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Sugars in high quantity (26.7%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of sugar can cause weight gain and tooth decay. It also augments the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardio-vascular diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of sugar and sugary drinks- Sugary drinks (such as sodas, fruit beverages, and fruit juices and nectars) should be limited as much as possible (no more than 1 glass a day).
- Choose products with lower sugar content and reduce the consumption of products with added sugars.
-
Salt in moderate quantity (1.08%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of salt (or sodium) can cause raised blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Many people who have high blood pressure do not know it, as there are often no symptoms.
- Most people consume too much salt (on average 9 to 12 grams per day), around twice the recommended maximum level of intake.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of salt and salted food- Reduce the quantity of salt used when cooking, and don't salt again at the table.
- Limit the consumption of salty snacks and choose products with lower salt content.
-
-
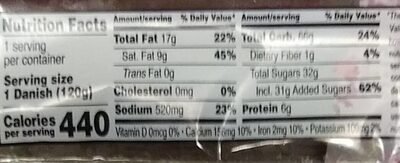
Nutrition facts
Nutrition facts As sold
for 100 g / 100 mlAs sold
per serving (1 DANISH (120 g))Compared to: Cakes Energy 1,536 kj
(367 kcal)1,840 kj
(440 kcal)-6% Fat 14.167 g 17 g -20% Saturated fat 7.5 g 9 g +12% Trans fat 0 g 0 g -100% Cholesterol 0 mg 0 mg -100% Carbohydrates 55 g 66 g +5% Sugars 26.667 g 32 g -9% Fiber 0.833 g 1 g -53% Proteins 5 g 6 g -2% Salt 1.083 g 1.3 g +57% Potassium 83 mg 99.6 mg -28% Calcium 125 mg 150 mg +156% Iron 1.83 mg 2.2 mg +7% Fruits‚ vegetables‚ nuts and rapeseed‚ walnut and olive oils (estimate from ingredients list analysis) 0.003 % 0.003 %
Environment
-
Eco-Score not computed - Unknown environmental impact
We could not compute the Eco-Score of this product as it is missing some data, could you help complete it?Could you add a precise product category so that we can compute the Eco-Score? Add a category
Packaging
-
Missing packaging information for this product
⚠ ️ The information about the packaging of this product is not filled in.Take a photo of the recycling information Take a photo of the recycling information
Transportation
-
Origins of ingredients
Missing origins of ingredients information
⚠ ️ The origins of the ingredients of this product are not indicated.
If they are indicated on the packaging, you can modify the product sheet and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.Add the origins of ingredients for this product Add the origins of ingredients for this product
Threatened species
-
Contains palm oil
Drives deforestation and threatens species such as the orangutan
Tropical forests in Asia, Africa and Latin America are destroyed to create and expand oil palm tree plantations. The deforestation contributes to climate change, and it endangers species such as the orangutan, the pigmy elephant and the Sumatran rhino.
Report a problem
-
Incomplete or incorrect information?
Category, labels, ingredients, allergens, nutritional information, photos etc.
If the information does not match the information on the packaging, please complete or correct it. Open Food Facts is a collaborative database, and every contribution is useful for all.
Data sources
Product added on by openfoodfacts-contributors
Last edit of product page on by foodless.
Product page also edited by ecoscore-impact-estimator, inf, kiliweb, org-database-usda, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlhZ8WsTZkxDjPSfSm0G35eiVErbDPehS2pSjPKs, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlmxJTuDmgB_PDQbRpkiylvW8FIT2Y-xvxoHDMqg, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvln1hXvzTkzOdBQDkmV2on_WnN5i5f9dUvaLXbKs.