Help us make food transparency the norm!
As a non-profit organization, we depend on your donations to continue informing consumers around the world about what they eat.
The food revolution starts with you!
Dzik Mango Energy - WK Dzik - 500 ml
Dzik Mango Energy - WK Dzik - 500 ml
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barcode: 5902176738853 (EAN / EAN-13)
Quantity: 500 ml
Brands: WK Dzik
Categories: Beverages, Carbonated drinks, Artificially sweetened beverages, Energy drinks, Energy drink without sugar and with artificial sweeteners
Countries where sold: Poland
Matching with your preferences
Health
Ingredients
-
31 ingredients
: Woda, wzmacniacz smaku: erytrytol, kwas: kwas cytrynowy, dwutlenek węgla, tauryna (0,4%), regulator kwasowości: cytryniany sodu; aromat, ekstrakt żeńszenia (0,08%), kofeina (0,04%), substancje słodzące (acesulfam K, sukraloza); stabilizatory (guma arabska, estry glicerolu i żywicy roślinnej); substancje konserwujące (sorbinian potasu, benzoesan sodu); barwniki (karoteny, antocyjany), L-winian L-karnityny (0,015%), inozytol (0,01%), witaminy (niacyna, kwas pantotenowy, witamina B6, witamina B12).
Food processing
-
Ultra processed foods
Elements that indicate the product is in the 4 - Ultra processed food and drink products group:
- Additive: E160a - Carotene
- Additive: E163 - Anthocyanins
- Additive: E290 - Carbon dioxide
- Additive: E414 - Acacia gum
- Additive: E445 - Glycerol esters of wood rosin
- Additive: E950 - Acesulfame k
- Additive: E955 - Sucralose
- Additive: E968 - Erythritol
- Ingredient: Colour
- Ingredient: Flavour enhancer
- Ingredient: Flavouring
- Ingredient: Sweetener
Food products are classified into 4 groups according to their degree of processing:
- Unprocessed or minimally processed foods
- Processed culinary ingredients
- Processed foods
- Ultra processed foods
The determination of the group is based on the category of the product and on the ingredients it contains.
Additives
-
E160a - Carotene
Carotene: The term carotene -also carotin, from the Latin carota, "carrot"- is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals -with the exception of some aphids and spider mites which acquired the synthesizing genes from fungi-. Carotenes are photosynthetic pigments important for photosynthesis. Carotenes contain no oxygen atoms. They absorb ultraviolet, violet, and blue light and scatter orange or red light, and -in low concentrations- yellow light. Carotenes are responsible for the orange colour of the carrot, for which this class of chemicals is named, and for the colours of many other fruits, vegetables and fungi -for example, sweet potatoes, chanterelle and orange cantaloupe melon-. Carotenes are also responsible for the orange -but not all of the yellow- colours in dry foliage. They also -in lower concentrations- impart the yellow coloration to milk-fat and butter. Omnivorous animal species which are relatively poor converters of coloured dietary carotenoids to colourless retinoids have yellowed-coloured body fat, as a result of the carotenoid retention from the vegetable portion of their diet. The typical yellow-coloured fat of humans and chickens is a result of fat storage of carotenes from their diets. Carotenes contribute to photosynthesis by transmitting the light energy they absorb to chlorophyll. They also protect plant tissues by helping to absorb the energy from singlet oxygen, an excited form of the oxygen molecule O2 which is formed during photosynthesis. β-Carotene is composed of two retinyl groups, and is broken down in the mucosa of the human small intestine by β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase to retinal, a form of vitamin A. β-Carotene can be stored in the liver and body fat and converted to retinal as needed, thus making it a form of vitamin A for humans and some other mammals. The carotenes α-carotene and γ-carotene, due to their single retinyl group -β-ionone ring-, also have some vitamin A activity -though less than β-carotene-, as does the xanthophyll carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin. All other carotenoids, including lycopene, have no beta-ring and thus no vitamin A activity -although they may have antioxidant activity and thus biological activity in other ways-. Animal species differ greatly in their ability to convert retinyl -beta-ionone- containing carotenoids to retinals. Carnivores in general are poor converters of dietary ionone-containing carotenoids. Pure carnivores such as ferrets lack β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase and cannot convert any carotenoids to retinals at all -resulting in carotenes not being a form of vitamin A for this species-; while cats can convert a trace of β-carotene to retinol, although the amount is totally insufficient for meeting their daily retinol needs.Source: Wikipedia
-
E163 - Anthocyanins
Anthocyanin: Anthocyanins -also anthocyans; from Greek: ἄνθος -anthos- "flower" and κυάνεος/κυανοῦς kyaneos/kyanous "dark blue"- are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, or blue. Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.Anthocyanins belong to a parent class of molecules called flavonoids synthesized via the phenylpropanoid pathway. They occur in all tissues of higher plants, including leaves, stems, roots, flowers, and fruits. Anthocyanins are derived from anthocyanidins by adding sugars. They are odorless and moderately astringent. Although approved to color foods and beverages in the European Union, anthocyanins are not approved for use as a food additive because they have not been verified as safe when used as food or supplement ingredients. There is no conclusive evidence anthocyanins have any effect on human biology or diseases.Source: Wikipedia
-
E202 - Potassium sorbate
Potassium sorbate (E202) is a synthetic food preservative commonly used to extend the shelf life of various food products.
It works by inhibiting the growth of molds, yeast, and some bacteria, preventing spoilage. When added to foods, it helps maintain their freshness and quality.
Some studies have shown that when combined with nitrites, potassium sorbate have genotoxic activity in vitro. However, potassium sorbate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory authorities.
-
E211 - Sodium benzoate
Sodium benzoate: Sodium benzoate is a substance which has the chemical formula NaC7H5O2. It is a widely used food preservative, with an E number of E211. It is the sodium salt of benzoic acid and exists in this form when dissolved in water. It can be produced by reacting sodium hydroxide with benzoic acid.Source: Wikipedia
-
E290 - Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide -chemical formula CO2- is a colorless gas with a density about 60% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide consists of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gas. The current concentration is about 0.04% -410 ppm- by volume, having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Natural sources include volcanoes, hot springs and geysers, and it is freed from carbonate rocks by dissolution in water and acids. Because carbon dioxide is soluble in water, it occurs naturally in groundwater, rivers and lakes, ice caps, glaciers and seawater. It is present in deposits of petroleum and natural gas. Carbon dioxide is odorless at normally encountered concentrations, however, at high concentrations, it has a sharp and acidic odor.As the source of available carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is the primary carbon source for life on Earth and its concentration in Earth's pre-industrial atmosphere since late in the Precambrian has been regulated by photosynthetic organisms and geological phenomena. Plants, algae and cyanobacteria use light energy to photosynthesize carbohydrate from carbon dioxide and water, with oxygen produced as a waste product.CO2 is produced by all aerobic organisms when they metabolize carbohydrates and lipids to produce energy by respiration. It is returned to water via the gills of fish and to the air via the lungs of air-breathing land animals, including humans. Carbon dioxide is produced during the processes of decay of organic materials and the fermentation of sugars in bread, beer and wine making. It is produced by combustion of wood and other organic materials and fossil fuels such as coal, peat, petroleum and natural gas. It is an unwanted byproduct in many large scale oxidation processes, for example, in the production of acrylic acid -over 5 million tons/year-.It is a versatile industrial material, used, for example, as an inert gas in welding and fire extinguishers, as a pressurizing gas in air guns and oil recovery, as a chemical feedstock and as a supercritical fluid solvent in decaffeination of coffee and supercritical drying. It is added to drinking water and carbonated beverages including beer and sparkling wine to add effervescence. The frozen solid form of CO2, known as dry ice is used as a refrigerant and as an abrasive in dry-ice blasting. Carbon dioxide is the most significant long-lived greenhouse gas in Earth's atmosphere. Since the Industrial Revolution anthropogenic emissions – primarily from use of fossil fuels and deforestation – have rapidly increased its concentration in the atmosphere, leading to global warming. Carbon dioxide also causes ocean acidification because it dissolves in water to form carbonic acid.Source: Wikipedia
-
E330 - Citric acid
Citric acid is a natural organic acid found in citrus fruits such as lemons, oranges, and limes.
It is widely used in the food industry as a flavor enhancer, acidulant, and preservative due to its tart and refreshing taste.
Citric acid is safe for consumption when used in moderation and is considered a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) food additive by regulatory agencies worldwide.
-
E331 - Sodium citrates
Sodium citrate: Sodium citrate may refer to any of the sodium salts of citrate -though most commonly the third-: Monosodium citrate Disodium citrate Trisodium citrateThe three forms of the salt are collectively known by the E number E331. Sodium citrates are used as acidity regulators in food and drinks, and also as emulsifiers for oils. They enable cheeses to melt without becoming greasy.Source: Wikipedia
-
E414 - Acacia gum
Gum arabic: Gum arabic, also known as acacia gum, arabic gum, gum acacia, acacia, Senegal gum and Indian gum, and by other names, is a natural gum consisting of the hardened sap of various species of the acacia tree. Originally, gum arabic was collected from Acacia nilotica which was called the "gum arabic tree"; in the present day, gum arabic is collected from acacia species, predominantly Acacia senegal and Vachellia -Acacia- seyal; the term "gum arabic" does not indicate a particular botanical source. In a few cases so‐called "gum arabic" may not even have been collected from Acacia species, but may originate from Combretum, Albizia or some other genus. Producers harvest the gum commercially from wild trees, mostly in Sudan -80%- and throughout the Sahel, from Senegal to Somalia—though it is historically cultivated in Arabia and West Asia. Gum arabic is a complex mixture of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. It is the original source of the sugars arabinose and ribose, both of which were first discovered and isolated from it, and are named after it. Gum arabic is soluble in water. It is edible, and used primarily in the food industry as a stabilizer, with EU E number E414. Gum arabic is a key ingredient in traditional lithography and is used in printing, paint production, glue, cosmetics and various industrial applications, including viscosity control in inks and in textile industries, though less expensive materials compete with it for many of these roles. While gum arabic is now produced throughout the African Sahel, it is still harvested and used in the Middle East.Source: Wikipedia
-
E445 - Glycerol esters of wood rosin
Glycerol ester of wood rosin: Glycerol ester of wood rosin, also known as glyceryl abietate or ester gum, is an oil-soluble food additive -E number E445-. The food-grade material is used in foods, beverages, and cosmetics to keep oils in suspension in water, and its name may be shortened in the ingredient list as glycerol ester of rosin. It is also used as an ingredient in the production of chewing-gum and ice cream. Similar, less pure materials -glycerol ester of gum rosin- are used as a component of certain low-cost adhesives.To make the glycerol ester of wood rosin, refined wood rosin is reacted with glycerin to produce the glycerol ester. Glycerol ester of wood rosin is an alternative to brominated vegetable oil in citrus oil-flavored soft drinks. In some cases, both ingredients are used together.Source: Wikipedia
-
E950 - Acesulfame k
Acesulfame potassium: Acesulfame potassium - AY-see-SUL-faym-, also known as acesulfame K -K is the symbol for potassium- or Ace K, is a calorie-free sugar substitute -artificial sweetener- often marketed under the trade names Sunett and Sweet One. In the European Union, it is known under the E number -additive code- E950. It was discovered accidentally in 1967 by German chemist Karl Clauss at Hoechst AG -now Nutrinova-. In chemical structure, acesulfame potassium is the potassium salt of 6-methyl-1‚2,3-oxathiazine-4-3H--one 2‚2-dioxide. It is a white crystalline powder with molecular formula C4H4KNO4S and a molecular weight of 201.24 g/mol.Source: Wikipedia
-
E955 - Sucralose
Sucralose: Sucralose is an artificial sweetener and sugar substitute. The majority of ingested sucralose is not broken down by the body, so it is noncaloric. In the European Union, it is also known under the E number E955. It is produced by chlorination of sucrose. Sucralose is about 320 to 1‚000 times sweeter than sucrose, three times as sweet as both aspartame and acesulfame potassium, and twice as sweet as sodium saccharin. Evidence of benefit is lacking for long-term weight loss with some data supporting weight gain and heart disease risks.It is stable under heat and over a broad range of pH conditions. Therefore, it can be used in baking or in products that require a long shelf life. The commercial success of sucralose-based products stems from its favorable comparison to other low-calorie sweeteners in terms of taste, stability, and safety. Common brand names of sucralose-based sweeteners are Splenda, Zerocal, Sukrana, SucraPlus, Candys, Cukren, and Nevella. Canderel Yellow also contains sucralose, but the original Canderel and Green Canderel do not.Source: Wikipedia
-
E968 - Erythritol
Erythritol: Erythritol --2R,3S--butane-1‚2,3‚4-tetrol- is a sugar alcohol -or polyol- that has been approved for use as a food additive in the United States and throughout much of the world. It was discovered in 1848 by Scottish chemist John Stenhouse. It occurs naturally in some fruit and fermented foods. At the industrial level, it is produced from glucose by fermentation with a yeast, Moniliella pollinis. Erythritol is 60–70% as sweet as sucrose -table sugar- yet it is almost noncaloric, does not affect blood sugar, does not cause tooth decay, and is partially absorbed by the body, excreted in urine and feces. Under U.S. Food and Drug Administration -FDA- labeling requirements, it has a caloric value of 0.2 kilocalories per gram -95% less than sugar and other carbohydrates-, though nutritional labeling varies from country to country. Some countries, such as Japan and the United States, label it as zero-calorie; the European Union labels it 0 kcal/g.Source: Wikipedia
Ingredients analysis
-
May contain palm oil
Ingredients that may contain palm oil: E160a
-
Non-vegan
Non-vegan ingredients: L-carnitine-L-tartrate
-
Vegetarian status unknown
Unrecognized ingredients: Vitamin b12
-
Details of the analysis of the ingredients
: Woda, wzmacniacz smaku (erytrytol), kwas (kwas cytrynowy), dwutlenek węgla, tauryna 0.4%, regulator kwasowości (cytryniany sodu), aromat, żeńszenia 0.08%, kofeina 0.04%, substancje słodzące (acesulfam K, sukraloza), stabilizatory (guma arabska, estry glicerolu i żywicy roślinnej), substancje konserwujące (sorbinian potasu, benzoesan sodu), barwniki (karoteny, antocyjany), L-winian L-karnityny 0.015%, inozytol 0.01%, witaminy, niacyna, kwas pantotenowy, witamina B6, witamina B12- Woda -> en:water - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 18066 - percent_min: 5 - percent_max: 98.035
- wzmacniacz smaku -> en:flavour-enhancer - percent_min: 0.4 - percent_max: 49.2175
- erytrytol -> en:e968 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0.4 - percent_max: 49.2175
- kwas -> en:acid - percent_min: 0.4 - percent_max: 32.945
- kwas cytrynowy -> en:e330 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0.4 - percent_max: 32.945
- dwutlenek węgla -> en:e290 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0.4 - percent_max: 24.80875
- tauryna -> en:taurine - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0.4 - percent: 0.4 - percent_max: 0.4
- regulator kwasowości -> en:acidity-regulator - percent_min: 0.08 - percent_max: 0.4
- cytryniany sodu -> en:e331 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.4
- aromat -> en:flavouring - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0.08 - percent_max: 0.4
- żeńszenia -> en:ginseng - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0.08 - percent: 0.08 - percent_max: 0.08
- kofeina -> en:caffeine - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0.04 - percent: 0.04 - percent_max: 0.04
- substancje słodzące -> en:sweetener - percent_min: 0.015 - percent_max: 0.04
- acesulfam K -> en:e950 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.04
- sukraloza -> en:e955 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.04
- stabilizatory -> en:stabiliser - percent_min: 0.015 - percent_max: 0.04
- guma arabska -> en:e414 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.04
- estry glicerolu i żywicy roślinnej -> en:e445 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.04
- substancje konserwujące -> en:preservative - percent_min: 0.015 - percent_max: 0.04
- sorbinian potasu -> en:e202 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.04
- benzoesan sodu -> en:e211 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.04
- barwniki -> en:colour - percent_min: 0.015 - percent_max: 0.04
- karoteny -> en:e160a - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - from_palm_oil: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.04
- antocyjany -> en:e163 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.04
- L-winian L-karnityny -> en:l-carnitine-l-tartrate - vegan: no - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0.015 - percent: 0.015 - percent_max: 0.015
- inozytol -> en:inositol - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0.01 - percent: 0.01 - percent_max: 0.01
- witaminy -> en:vitamins - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.01
- niacyna -> en:e375 - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.01
- kwas pantotenowy -> en:pantothenic-acid - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.01
- witamina B6 -> en:vitamin-b6 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.01
- witamina B12 -> en:vitamin-b12 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.01
Nutrition
-
Good nutritional quality
⚠ ️Warning: the amount of fruits, vegetables and nuts is not specified on the label, it was estimated from the list of ingredients: 0This product is considered a beverage for the calculation of the Nutri-Score.
Positive points: 0
- Proteins: 0 / 5 (value: 0.1, rounded value: 0.1)
- Fiber: 0 / 5 (value: 0, rounded value: 0)
- Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and colza/walnut/olive oils: 0 / 10 (value: 0, rounded value: 0)
Negative points: 1
- Energy: 1 / 10 (value: 14, rounded value: 14)
- Sugars: 0 / 10 (value: 0, rounded value: 0)
- Saturated fat: 0 / 10 (value: 0.02, rounded value: 0)
- Sodium: 0 / 10 (value: 80, rounded value: 80)
The points for proteins are counted because the negative points are less than 11.
Nutritional score: (1 - 0)
Nutri-Score:
-
Nutrient levels
-
Fat in low quantity (0.1%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Saturated fat in low quantity (0.02%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Sugars in low quantity (0%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of sugar can cause weight gain and tooth decay. It also augments the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardio-vascular diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of sugar and sugary drinks- Sugary drinks (such as sodas, fruit beverages, and fruit juices and nectars) should be limited as much as possible (no more than 1 glass a day).
- Choose products with lower sugar content and reduce the consumption of products with added sugars.
-
Salt in moderate quantity (0.2%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of salt (or sodium) can cause raised blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Many people who have high blood pressure do not know it, as there are often no symptoms.
- Most people consume too much salt (on average 9 to 12 grams per day), around twice the recommended maximum level of intake.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of salt and salted food- Reduce the quantity of salt used when cooking, and don't salt again at the table.
- Limit the consumption of salty snacks and choose products with lower salt content.
-
-
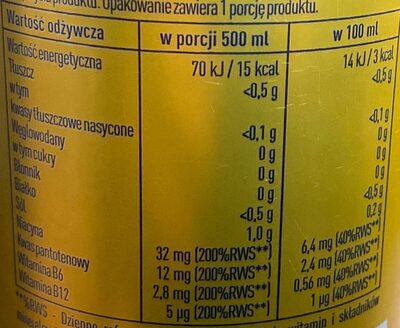
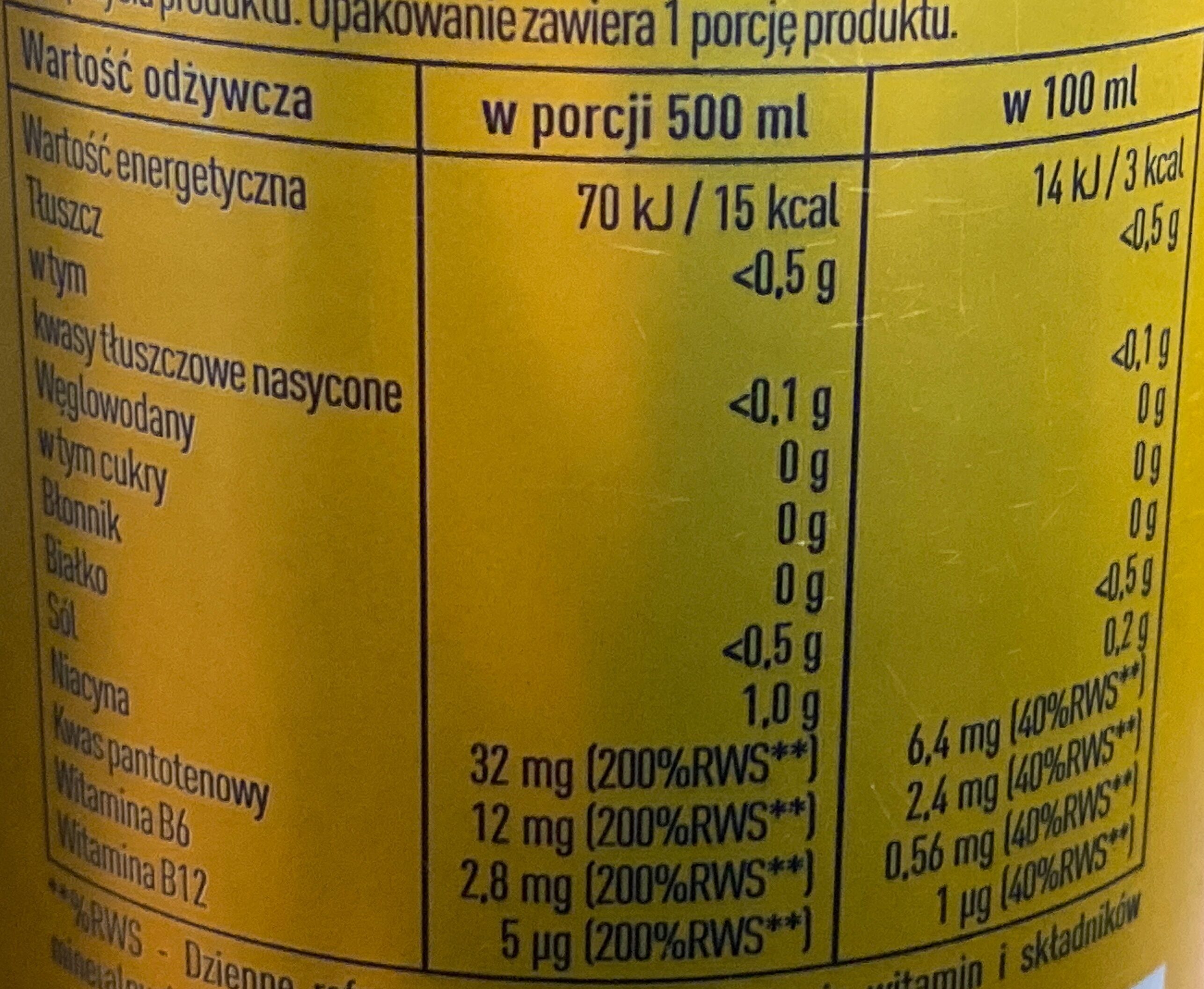
Nutrition facts
Nutrition facts As sold
for 100 g / 100 mlAs sold
per serving (500 ml)Compared to: Energy drink without sugar and with artificial sweeteners Energy 14 kj
(3 kcal)70 kj
(15 kcal)-42% Fat < 0.1 g < 0.5 g +213% Saturated fat < 0.02 g < 0.1 g +194% Carbohydrates 0 g 0 g -100% Sugars 0 g 0 g -100% Fiber 0 g 0 g -100% Proteins < 0.1 g < 0.5 g +1% Salt 0.2 g 1 g +61% Vitamin B3/PP (Niacin) 6.4 mg 32 mg -12% Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxin) 0.56 mg 2.8 mg -29% Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) 1 µg 5 µg -61% Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) 2.4 mg 12 mg -23% Caffeine 40 mg 200 mg +3% Fruits‚ vegetables‚ nuts and rapeseed‚ walnut and olive oils (estimate from ingredients list analysis) 0 % 0 %
Environment
-
Eco-Score not yet applicable
Not yet applicable for the category: Energy drinks
The Eco-Score is not yet applicable for this category, but we are working on adding support for it.
Packaging
-
Missing packaging information for this product
⚠ ️ The information about the packaging of this product is not filled in.Take a photo of the recycling information Take a photo of the recycling information
Transportation
-
Origins of ingredients
Missing origins of ingredients information
⚠ ️ The origins of the ingredients of this product are not indicated.
If they are indicated on the packaging, you can modify the product sheet and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.Add the origins of ingredients for this product Add the origins of ingredients for this product
Report a problem
-
Incomplete or incorrect information?
Category, labels, ingredients, allergens, nutritional information, photos etc.
If the information does not match the information on the packaging, please complete or correct it. Open Food Facts is a collaborative database, and every contribution is useful for all.
Data sources
Product added on by smoothie-app
Last edit of product page on by arc2.
Product page also edited by annelotte, danis1597, darrro.