Help us make food transparency the norm!
As a non-profit organization, we depend on your donations to continue informing consumers around the world about what they eat.
The food revolution starts with you!
Vegetarian Mushroom Flavour - Myojo - 80 g
Vegetarian Mushroom Flavour - Myojo - 80 g
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barcode: 8888107000299 (EAN / EAN-13)
Quantity: 80 g
Packaging: Plastic
Categories: Plant-based foods and beverages, Plant-based foods, Cereals and potatoes, Cereals and their products, Dried products, Pastas, Dried products to be rehydrated, Noodles, Instant noodles
Labels, certifications, awards: Vegetarian
Manufacturing or processing places: Indonesia
Stores: NTUC Fairprice
Countries where sold: Singapore
Matching with your preferences
Health
Ingredients
-
45 ingredients
NOODLES: Wheat flour (contains iron, zinc, vitamins [B2, B1, folic acid]) (78%), palm oil (antioxidants [307b, 320, 321]), salt, acidity regulators (450, 451, 501, 500, stabilisers (412, 414), colour (160a), emulsifier (1450). SEASONING POWDER: Salt, flavour enhancers (621, 635), vegetables powder (mushroom, carrot, cabbage), sugar, hydrolysed plant protein (soya, stabiliser [1400]), sesame oil, colour (150c), anticaking agent (551). This product contains wheat, soya, sesame.Allergens: Gluten, Sesame seeds, SoybeansTraces: Gluten, Sesame seeds, Soybeans
Food processing
-
Ultra processed foods
Elements that indicate the product is in the 4 - Ultra processed food and drink products group:
- Additive: E1400 - Dextrin
- Additive: E1450 - Starch sodium octenyl succinate
- Additive: E150c - Ammonia caramel
- Additive: E160a - Carotene
- Additive: E412 - Guar gum
- Additive: E414 - Acacia gum
- Additive: E450 - Diphosphates
- Additive: E451 - Triphosphates
- Additive: E551 - Silicon dioxide
- Additive: E621 - Monosodium glutamate
- Additive: E635 - Disodium 5'-ribonucleotide
- Ingredient: Colour
- Ingredient: Emulsifier
- Ingredient: Flavour enhancer
Food products are classified into 4 groups according to their degree of processing:
- Unprocessed or minimally processed foods
- Processed culinary ingredients
- Processed foods
- Ultra processed foods
The determination of the group is based on the category of the product and on the ingredients it contains.
Additives
-
E1400 - Dextrin
Dextrin: Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch or glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α--1→4- or α--1→6- glycosidic bonds. Dextrins can be produced from starch using enzymes like amylases, as during digestion in the human body and during malting and mashing, or by applying dry heat under acidic conditions -pyrolysis or roasting-. The latter process is used industrially, and also occurs on the surface of bread during the baking process, contributing to flavor, color and crispness. Dextrins produced by heat are also known as pyrodextrins. The starch hydrolyses during roasting under acidic conditions, and short-chained starch parts partially rebranch with α--1‚6- bonds to the degraded starch molecule. See also Maillard Reaction. Dextrins are white, yellow, or brown powders that are partially or fully water-soluble, yielding optically active solutions of low viscosity. Most of them can be detected with iodine solution, giving a red coloration; one distinguishes erythrodextrin -dextrin that colours red- and achrodextrin -giving no colour-. White and yellow dextrins from starch roasted with little or no acid are called British gum.Source: Wikipedia
-
E160a - Carotene
Carotene: The term carotene -also carotin, from the Latin carota, "carrot"- is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals -with the exception of some aphids and spider mites which acquired the synthesizing genes from fungi-. Carotenes are photosynthetic pigments important for photosynthesis. Carotenes contain no oxygen atoms. They absorb ultraviolet, violet, and blue light and scatter orange or red light, and -in low concentrations- yellow light. Carotenes are responsible for the orange colour of the carrot, for which this class of chemicals is named, and for the colours of many other fruits, vegetables and fungi -for example, sweet potatoes, chanterelle and orange cantaloupe melon-. Carotenes are also responsible for the orange -but not all of the yellow- colours in dry foliage. They also -in lower concentrations- impart the yellow coloration to milk-fat and butter. Omnivorous animal species which are relatively poor converters of coloured dietary carotenoids to colourless retinoids have yellowed-coloured body fat, as a result of the carotenoid retention from the vegetable portion of their diet. The typical yellow-coloured fat of humans and chickens is a result of fat storage of carotenes from their diets. Carotenes contribute to photosynthesis by transmitting the light energy they absorb to chlorophyll. They also protect plant tissues by helping to absorb the energy from singlet oxygen, an excited form of the oxygen molecule O2 which is formed during photosynthesis. β-Carotene is composed of two retinyl groups, and is broken down in the mucosa of the human small intestine by β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase to retinal, a form of vitamin A. β-Carotene can be stored in the liver and body fat and converted to retinal as needed, thus making it a form of vitamin A for humans and some other mammals. The carotenes α-carotene and γ-carotene, due to their single retinyl group -β-ionone ring-, also have some vitamin A activity -though less than β-carotene-, as does the xanthophyll carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin. All other carotenoids, including lycopene, have no beta-ring and thus no vitamin A activity -although they may have antioxidant activity and thus biological activity in other ways-. Animal species differ greatly in their ability to convert retinyl -beta-ionone- containing carotenoids to retinals. Carnivores in general are poor converters of dietary ionone-containing carotenoids. Pure carnivores such as ferrets lack β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase and cannot convert any carotenoids to retinals at all -resulting in carotenes not being a form of vitamin A for this species-; while cats can convert a trace of β-carotene to retinol, although the amount is totally insufficient for meeting their daily retinol needs.Source: Wikipedia
-
E307b - Concentrated tocopherol
Alpha-Tocopherol: α-Tocopherol is a type of vitamin E. It has E number "E307". Vitamin E exists in eight different forms, four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. All feature a chromane ring, with a hydroxyl group that can donate a hydrogen atom to reduce free radicals and a hydrophobic side chain which allows for penetration into biological membranes. Compared to the others, α-tocopherol is preferentially absorbed and accumulated in humans.Source: Wikipedia
-
E320 - Butylated hydroxyanisole (bha)
Butylated hydroxyanisole: Butylated hydroxyanisole -BHA- is an antioxidant consisting of a mixture of two isomeric organic compounds, 2-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole and 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole. It is prepared from 4-methoxyphenol and isobutylene. It is a waxy solid used as a food additive with the E number E320. The primary use for BHA is as an antioxidant and preservative in food, food packaging, animal feed, cosmetics, rubber, and petroleum products. BHA also is commonly used in medicines, such as isotretinoin, lovastatin, and simvastatin, among others.Source: Wikipedia
-
E321 - Butylated hydroxytoluene
Butylated hydroxytoluene: Butylated hydroxytoluene -BHT-, also known as dibutylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound, chemically a derivative of phenol, that is useful for its antioxidant properties. European and U.S. regulations allow small amounts to be used as a food additive. In addition to this use, BHT is widely used to prevent oxidation in fluids -e.g. fuel, oil- and other materials where free radicals must be controlled.Source: Wikipedia
-
E412 - Guar gum
Guar gum (E412) is a natural food additive derived from guar beans.
This white, odorless powder is valued for its remarkable thickening and stabilizing properties, making it a common ingredient in various food products, including sauces, dressings, and ice creams.
When used in moderation, guar gum is considered safe for consumption, with no known adverse health effects.
-
E414 - Acacia gum
Gum arabic: Gum arabic, also known as acacia gum, arabic gum, gum acacia, acacia, Senegal gum and Indian gum, and by other names, is a natural gum consisting of the hardened sap of various species of the acacia tree. Originally, gum arabic was collected from Acacia nilotica which was called the "gum arabic tree"; in the present day, gum arabic is collected from acacia species, predominantly Acacia senegal and Vachellia -Acacia- seyal; the term "gum arabic" does not indicate a particular botanical source. In a few cases so‐called "gum arabic" may not even have been collected from Acacia species, but may originate from Combretum, Albizia or some other genus. Producers harvest the gum commercially from wild trees, mostly in Sudan -80%- and throughout the Sahel, from Senegal to Somalia—though it is historically cultivated in Arabia and West Asia. Gum arabic is a complex mixture of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. It is the original source of the sugars arabinose and ribose, both of which were first discovered and isolated from it, and are named after it. Gum arabic is soluble in water. It is edible, and used primarily in the food industry as a stabilizer, with EU E number E414. Gum arabic is a key ingredient in traditional lithography and is used in printing, paint production, glue, cosmetics and various industrial applications, including viscosity control in inks and in textile industries, though less expensive materials compete with it for many of these roles. While gum arabic is now produced throughout the African Sahel, it is still harvested and used in the Middle East.Source: Wikipedia
-
E450 - Diphosphates
Diphosphates (E450) are food additives often utilized to modify the texture of products, acting as leavening agents in baking and preventing the coagulation of canned food.
These salts can stabilize whipped cream and are also found in powdered products to maintain their flow properties. They are commonly present in baked goods, processed meats, and soft drinks.
Derived from phosphoric acid, they're part of our daily phosphate intake, which often surpasses recommended levels due to the prevalence of phosphates in processed foods and drinks.
Excessive phosphate consumption is linked to health issues, such as impaired kidney function and weakened bone health. Though diphosphates are generally regarded as safe when consumed within established acceptable daily intakes, it's imperative to monitor overall phosphate consumption to maintain optimal health.
-
E451 - Triphosphates
Sodium triphosphate: Sodium triphosphate -STP-, also sodium tripolyphosphate -STPP-, or tripolyphosphate -TPP-,- is an inorganic compound with formula Na5P3O10. It is the sodium salt of the polyphosphate penta-anion, which is the conjugate base of triphosphoric acid. It is produced on a large scale as a component of many domestic and industrial products, especially detergents. Environmental problems associated with eutrophication are attributed to its widespread use.Source: Wikipedia
-
E500 - Sodium carbonates
Sodium carbonates (E500) are compounds commonly used in food preparation as leavening agents, helping baked goods rise by releasing carbon dioxide when they interact with acids.
Often found in baking soda, they regulate the pH of food, preventing it from becoming too acidic or too alkaline. In the culinary world, sodium carbonates can also enhance the texture and structure of foods, such as noodles, by modifying the gluten network.
Generally recognized as safe, sodium carbonates are non-toxic when consumed in typical amounts found in food.
-
E501 - Potassium carbonates
Potassium carbonate: Potassium carbonate -K2CO3- is a white salt, which is soluble in water -insoluble in ethanol- and forms a strongly alkaline solution. It can be made as the product of potassium hydroxide's absorbent reaction with carbon dioxide. It is deliquescent, often appearing a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is used in the production of soap and glass.Source: Wikipedia
-
E551 - Silicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide: Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, silicic acid or silicic acid anydride is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula SiO2, most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics -as an electrical insulator-, and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Inhaling finely divided crystalline silica is toxic and can lead to severe inflammation of the lung tissue, silicosis, bronchitis, lung cancer, and systemic autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Uptake of amorphous silicon dioxide, in high doses, leads to non-permanent short-term inflammation, where all effects heal.Source: Wikipedia
-
E621 - Monosodium glutamate
Monosodium glutamate: Monosodium glutamate -MSG, also known as sodium glutamate- is the sodium salt of glutamic acid, one of the most abundant naturally occurring non-essential amino acids. Glutamic acid is found naturally in tomatoes, grapes, cheese, mushrooms and other foods.MSG is used in the food industry as a flavor enhancer with an umami taste that intensifies the meaty, savory flavor of food, as naturally occurring glutamate does in foods such as stews and meat soups. It was first prepared in 1908 by Japanese biochemist Kikunae Ikeda, who was trying to isolate and duplicate the savory taste of kombu, an edible seaweed used as a base for many Japanese soups. MSG as a flavor enhancer balances, blends, and rounds the perception of other tastes.The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has given MSG its generally recognized as safe -GRAS- designation. A popular belief is that large doses of MSG can cause headaches and other feelings of discomfort, known as "Chinese restaurant syndrome," but double-blind tests fail to find evidence of such a reaction. The European Union classifies it as a food additive permitted in certain foods and subject to quantitative limits. MSG has the HS code 29224220 and the E number E621.Source: Wikipedia
Ingredients analysis
-
Palm oil
Ingredients that contain palm oil: Palm oil
-
Vegan status unknown
Unrecognized ingredients: Iron, Zinc, Thiamin, Folic acid, 307b, 320, 321, 450, 451, 501, 500, 412, 414, 160a, 1450, 621, 635, 1400, 150c, 551Some ingredients could not be recognized.
We need your help!
You can help us recognize more ingredients and better analyze the list of ingredients for this product and others:
- Edit this product page to correct spelling mistakes in the ingredients list, and/or to remove ingredients in other languages and sentences that are not related to the ingredients.
- Add new entries, synonyms or translations to our multilingual lists of ingredients, ingredient processing methods, and labels.
If you would like to help, join the #ingredients channel on our Slack discussion space and/or learn about ingredients analysis on our wiki. Thank you!
-
Vegetarian
No non-vegetarian ingredients detected
Unrecognized ingredients: Iron, Zinc, Thiamin, Folic acid, 307b, 320, 321, 450, 451, 501, 500, 412, 414, 160a, 1450, 621, 635, 1400, 150c, 551Some ingredients could not be recognized.
We need your help!
You can help us recognize more ingredients and better analyze the list of ingredients for this product and others:
- Edit this product page to correct spelling mistakes in the ingredients list, and/or to remove ingredients in other languages and sentences that are not related to the ingredients.
- Add new entries, synonyms or translations to our multilingual lists of ingredients, ingredient processing methods, and labels.
If you would like to help, join the #ingredients channel on our Slack discussion space and/or learn about ingredients analysis on our wiki. Thank you!
-
Details of the analysis of the ingredients
We need your help!
Some ingredients could not be recognized.
We need your help!
You can help us recognize more ingredients and better analyze the list of ingredients for this product and others:
- Edit this product page to correct spelling mistakes in the ingredients list, and/or to remove ingredients in other languages and sentences that are not related to the ingredients.
- Add new entries, synonyms or translations to our multilingual lists of ingredients, ingredient processing methods, and labels.
If you would like to help, join the #ingredients channel on our Slack discussion space and/or learn about ingredients analysis on our wiki. Thank you!
: NOODLES (Wheat flour, contains iron), zinc, vitamins, vitamin B2, vitamin B1, folic acid 78%, palm oil (antioxidants (307b, 320, 321)), salt, acidity regulators, 450, 451, 501, 500, stabilisers (412, 414), colour (160a), emulsifier (1450), SEASONING (Salt), flavour enhancers (621, 635), vegetables (mushroom, carrot, cabbage), sugar, hydrolysed plant protein (soya, stabiliser (1400)), sesame oil, colour (150c), anticaking agent (551)- NOODLES -> en:noodle - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe
- Wheat flour -> en:wheat-flour - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9410
- contains iron -> en:iron
- zinc -> en:zinc
- vitamins -> en:vitamins - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes
- vitamin B2 -> en:e101 - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: yes
- vitamin B1 -> en:thiamin
- folic acid -> en:folic-acid - percent: 78
- palm oil -> en:palm-oil - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - from_palm_oil: yes - ciqual_food_code: 16129
- antioxidants -> en:antioxidant
- 307b -> en:307b
- 320 -> en:320
- 321 -> en:321
- antioxidants -> en:antioxidant
- salt -> en:salt - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 11058
- acidity regulators -> en:acidity-regulator
- 450 -> en:450
- 451 -> en:451
- 501 -> en:501
- 500 -> en:500
- stabilisers -> en:stabiliser
- 412 -> en:412
- 414 -> en:414
- colour -> en:colour
- 160a -> en:160a
- emulsifier -> en:emulsifier
- 1450 -> en:1450
- SEASONING -> en:coating - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe
- Salt -> en:salt - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 11058
- flavour enhancers -> en:flavour-enhancer
- 621 -> en:621
- 635 -> en:635
- vegetables -> en:vegetable - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes
- mushroom -> en:mushroom - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 20010
- carrot -> en:carrot - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 20009
- cabbage -> en:cabbage - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes
- sugar -> en:sugar - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 31016
- hydrolysed plant protein -> en:hydrolysed-vegetable-protein - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes
- soya -> en:soya - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes
- stabiliser -> en:stabiliser
- 1400 -> en:1400
- sesame oil -> en:sesame-oil - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - from_palm_oil: no - ciqual_food_code: 17400
- colour -> en:colour
- 150c -> en:150c
- anticaking agent -> en:anti-caking-agent
- 551 -> en:551
-
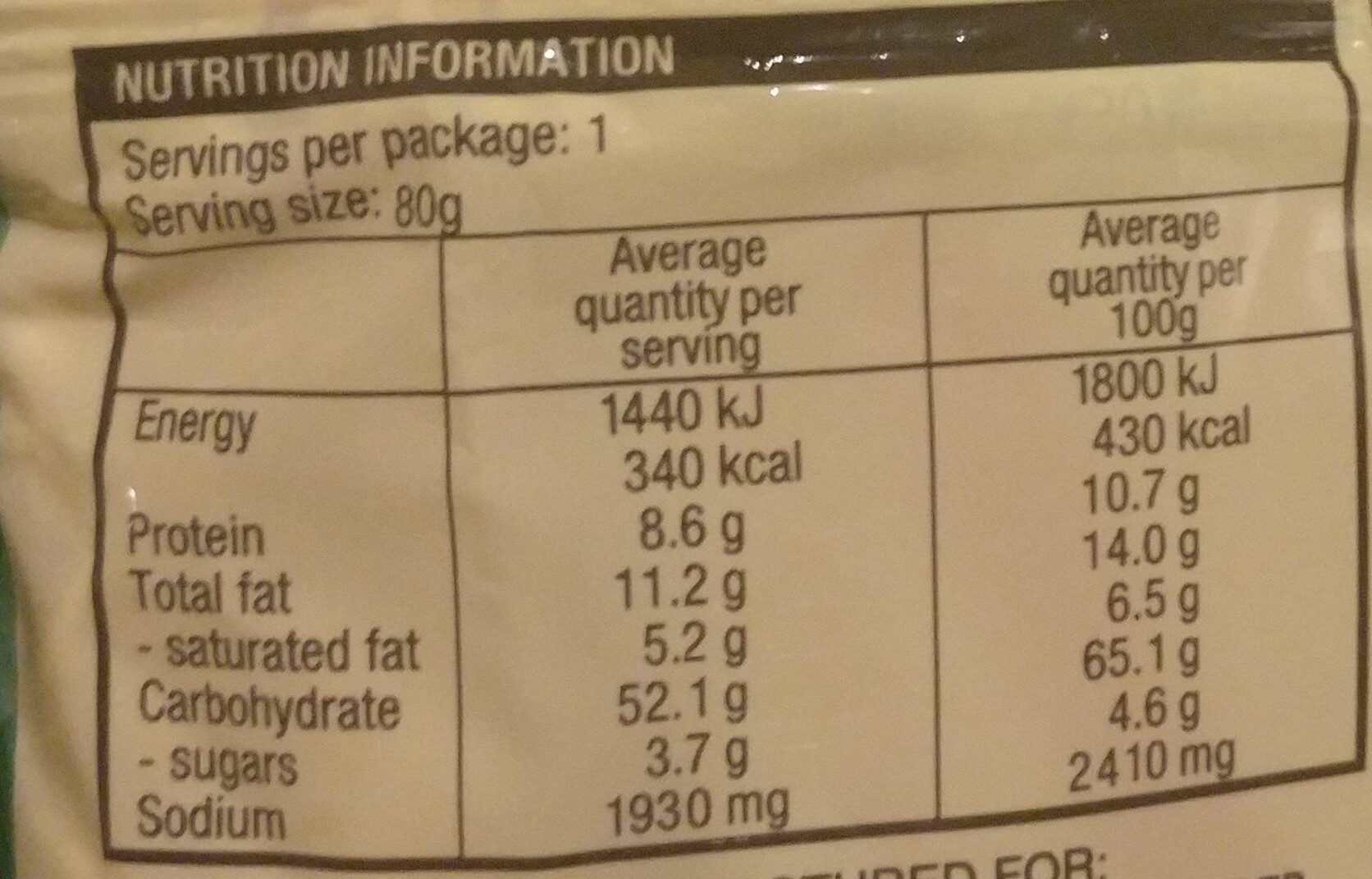
Nutrition facts
Nutrition facts As sold
for 100 g / 100 mlAs sold
per serving (80g)Compared to: Instant noodles Energy 1,799 kj
(430 kcal)1,440 kj
(344 kcal)+43% Fat 14 g 11.2 g +25% Saturated fat 6.5 g 5.2 g +31% Carbohydrates 65.1 g 52.1 g +55% Sugars 4.6 g 3.68 g +80% Fiber ? ? Proteins 10.7 g 8.56 g +64% Salt 6.025 g 4.82 g +129% Fruits‚ vegetables‚ nuts and rapeseed‚ walnut and olive oils (estimate from ingredients list analysis) 0 % 0 %
Environment
-
Eco-Score C - Moderate environmental impact
⚠ ️Select a country in order to include the full impact of transportation.The Eco-Score is an experimental score that summarizes the environmental impacts of food products.→ The Eco-Score was initially developped for France and it is being extended to other European countries. The Eco-Score formula is subject to change as it is regularly improved to make it more precise and better suited to each country.Life cycle analysis
-
Average impact of products of the same category: A (Score: 82/100)
Category: Asian noodles, flavoured, dehydrated
Category: Asian noodles, flavoured, dehydrated
- PEF environmental score: 0.26 (the lower the score, the lower the impact)
- including impact on climate change: 1.67 kg CO2 eq/kg of product
Stage Impact Agriculture
65.5 %Processing
20.6 %Packaging
8.7 %Transportation
3.5 %Distribution
1.8 %Consumption
0.0 %
Bonuses and maluses
-
Missing origins of ingredients information
Malus: -5
⚠ ️ The origins of the ingredients of this product are not indicated.
If they are indicated on the packaging, you can modify the product sheet and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.
-
Ingredients that threatens species
Malus: -10
Contains palm oil
Tropical forests in Asia, Africa and Latin America are destroyed to create and expand oil palm tree plantations. The deforestation contributes to climate change, and it endangers species such as the orangutan, the pigmy elephant and the Sumatran rhino.
-
Packaging with a medium impact
Malus: -10
Shape Material Recycling Impact Unknown Plastic High ⚠ ️ The information about the packaging of this product is not sufficiently precise (exact shapes and materials of all components of the packaging).⚠ ️ For a more precise calculation of the Eco-Score, you can modify the product page and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.
Eco-Score for this product
-
Impact for this product: C (Score: 57/100)
Product: Vegetarian Mushroom Flavour - Myojo - 80 g
Life cycle analysis score: 82
Sum of bonuses and maluses: -25
Final score: 57/100
-
Carbon footprint
-
Equal to driving 0.9 km in a petrol car
167 g CO² per 100g of product
The carbon emission figure comes from ADEME's Agribalyse database, for the category: Asian noodles, flavoured, dehydrated (Source: ADEME Agribalyse Database)
Stage Impact Agriculture
61.0 %Processing
14.9 %Packaging
16.3 %Transportation
6.8 %Distribution
1.0 %Consumption
0.0 %
Packaging
-
Packaging with a medium impact
-
Packaging parts
(Plastic)
-
Packaging materials
Material % Packaging weight Packaging weight per 100 g of product Plastic
-
Transportation
-
Origins of ingredients
Missing origins of ingredients information
⚠ ️ The origins of the ingredients of this product are not indicated.
If they are indicated on the packaging, you can modify the product sheet and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.Add the origins of ingredients for this product Add the origins of ingredients for this product
Threatened species
-
Contains palm oil
Drives deforestation and threatens species such as the orangutan
Tropical forests in Asia, Africa and Latin America are destroyed to create and expand oil palm tree plantations. The deforestation contributes to climate change, and it endangers species such as the orangutan, the pigmy elephant and the Sumatran rhino.
Report a problem
-
Incomplete or incorrect information?
Category, labels, ingredients, allergens, nutritional information, photos etc.
If the information does not match the information on the packaging, please complete or correct it. Open Food Facts is a collaborative database, and every contribution is useful for all.
Data sources
Product added on by bcd4e6
Last edit of product page on by packbot.
Product page also edited by openfoodfacts-contributors, vaporous.