Help us make food transparency the norm!
As a non-profit organization, we depend on your donations to continue informing consumers around the world about what they eat.
The food revolution starts with you!
Gerble - Soya Fig Cookie, 270g (9.6oz) - 270 g
Gerble - Soya Fig Cookie, 270g (9.6oz) - 270 g
Barcode: 3175681851863 (EAN / EAN-13)
Common name: Biscuits au soja et à la figue, riches en magnésium, vitamines E, B1 et B9, et source de calcium, fer, vitamines B5, B6 et PP.
Quantity: 270 g
Packaging: fr:1 étui en carton à recycler, fr:4 sachets en plastiques à recycler
Brands: Gerblé
Categories: Snacks, Sweet snacks, Biscuits and cakes, Biscuits
Labels, certifications, awards: No GMOs, Made in France, No palm oil, Nutriscore, Nutriscore Grade B, fr:Farine-de-ble-filiere-durable
Origin of ingredients: France, fr:Annonay, fr:Figues origine non-Union Européenne, fr:Germe de blé origine Union Européenne, fr:Haute-Garonne, fr:Soja origine Union Européenne
Stores: Spar, Magasins U, Delhaize, carrefour.fr, Leclerc
Countries where sold: Belgium, France, Morocco, Réunion, Switzerland
Matching with your preferences
Health
Ingredients
-
22 ingredients
wheat flour, brown cane sugar, rapeseed oil, whole wheat flour, soybean flakes 10.4%, fig paste 7%, wheat germ 5.6%, wheat starch, emulsifier: rapeseed lecithins, magnesium, natural flavor, baking powders (citric acid, sodium carbonates), vitamins (e, pp, b5, b6, b1, b9), made in a workshop that uses nuts, milk, sesame and lupineAllergens: Gluten, Milk, SoybeansTraces: Eggs, Lupin, Milk, Nuts, Sesame seeds
Food processing
-
Ultra processed foods
Elements that indicate the product is in the 4 - Ultra processed food and drink products group:
- Additive: E322 - Lecithins
- Ingredient: Emulsifier
- Ingredient: Flavouring
Food products are classified into 4 groups according to their degree of processing:
- Unprocessed or minimally processed foods
- Processed culinary ingredients
- Processed foods
- Ultra processed foods
The determination of the group is based on the category of the product and on the ingredients it contains.
Additives
-
E322 - Lecithins
Lecithins are natural compounds commonly used in the food industry as emulsifiers and stabilizers.
Extracted from sources like soybeans and eggs, lecithins consist of phospholipids that enhance the mixing of oil and water, ensuring smooth textures in various products like chocolates, dressings, and baked goods.
They do not present any known health risks.
-
E322i - Lecithin
Lecithins are natural compounds commonly used in the food industry as emulsifiers and stabilizers.
Extracted from sources like soybeans and eggs, lecithins consist of phospholipids that enhance the mixing of oil and water, ensuring smooth textures in various products like chocolates, dressings, and baked goods.
They do not present any known health risks.
-
E330 - Citric acid
Citric acid is a natural organic acid found in citrus fruits such as lemons, oranges, and limes.
It is widely used in the food industry as a flavor enhancer, acidulant, and preservative due to its tart and refreshing taste.
Citric acid is safe for consumption when used in moderation and is considered a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) food additive by regulatory agencies worldwide.
-
E500 - Sodium carbonates
Sodium carbonates (E500) are compounds commonly used in food preparation as leavening agents, helping baked goods rise by releasing carbon dioxide when they interact with acids.
Often found in baking soda, they regulate the pH of food, preventing it from becoming too acidic or too alkaline. In the culinary world, sodium carbonates can also enhance the texture and structure of foods, such as noodles, by modifying the gluten network.
Generally recognized as safe, sodium carbonates are non-toxic when consumed in typical amounts found in food.
Ingredients analysis
-
Palm oil free
No ingredients containing palm oil detected
-
Vegan status unknown
Unrecognized ingredients: Magnesium, Vitamin E, Thiamin, Folic acid
-
Vegetarian status unknown
Unrecognized ingredients: Magnesium, Vitamin E, Thiamin, Folic acid
-
Details of the analysis of the ingredients
fr: Farine de _blé_, sucre de canne roux, huile de colza, farine complète de _blé_, _soja_ 10.4%, pâte de figues 7%, germe de _blé_ 5.6%, amidon de _blé_, émulsifiant (lécithines de colza), magnésium, arôme naturel, poudres à lever (acide citrique, carbonates de sodium), vitamines, vitamine E, vitamine PP, vitamine B5, vitamine B6, vitamine B1, vitamine B9- Farine de _blé_ -> en:wheat-flour - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9410 - percent_min: 10.4 - percent_max: 45.8
- sucre de canne roux -> en:unrefined-cane-sugar - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 31016 - percent_min: 10.4 - percent_max: 17
- huile de colza -> en:colza-oil - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - from_palm_oil: no - ciqual_food_code: 17130 - percent_min: 10.4 - percent_max: 17
- farine complète de _blé_ -> en:whole-wheat-flour - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9410 - percent_min: 10.4 - percent_max: 17
- _soja_ -> en:soya - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 10.4 - percent: 10.4 - percent_max: 10.4
- pâte de figues -> en:fig-paste - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13012 - percent_min: 7 - percent: 7 - percent_max: 7
- germe de _blé_ -> en:wheat-germ - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 9660 - percent_min: 5.6 - percent: 5.6 - percent_max: 5.6
- amidon de _blé_ -> en:wheat-starch - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9510 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5.6
- émulsifiant -> en:emulsifier - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5.6
- lécithines de colza -> en:rapeseed-lecithin - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5.6
- magnésium -> en:magnesium - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5.6
- arôme naturel -> en:natural-flavouring - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- poudres à lever -> en:raising-agent - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 4.58
- acide citrique -> en:e330 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 4.58
- carbonates de sodium -> en:e500 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 2.29
- vitamines -> en:vitamins - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 4.16363636363636
- vitamine E -> en:vitamin-e - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 3.81666666666667
- vitamine PP -> en:e375 - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 3.52307692307692
- vitamine B5 -> en:pantothenic-acid - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 3.27142857142857
- vitamine B6 -> en:vitamin-b6 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 3.05333333333333
- vitamine B1 -> en:thiamin - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 2.8625
- vitamine B9 -> en:folic-acid - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 2.69411764705882
Nutrition
-
Good nutritional quality
⚠ ️Warning: the amount of fruits, vegetables and nuts is not specified on the label, it was estimated from the list of ingredients: 20This product is not considered a beverage for the calculation of the Nutri-Score.
Positive points: 10
- Proteins: 5 / 5 (value: 12, rounded value: 12)
- Fiber: 5 / 5 (value: 5.6, rounded value: 5.6)
- Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and colza/walnut/olive oils: 0 / 5 (value: 20.7, rounded value: 20.7)
Negative points: 10
- Energy: 5 / 10 (value: 1878, rounded value: 1878)
- Sugars: 3 / 10 (value: 17, rounded value: 17)
- Saturated fat: 1 / 10 (value: 1.7, rounded value: 1.7)
- Sodium: 1 / 10 (value: 144, rounded value: 144)
The points for proteins are counted because the negative points are less than 11.
Nutritional score: (10 - 10)
Nutri-Score:
-
Nutrient levels
-
Fat in moderate quantity (16%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Saturated fat in moderate quantity (1.7%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Sugars in high quantity (17%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of sugar can cause weight gain and tooth decay. It also augments the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardio-vascular diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of sugar and sugary drinks- Sugary drinks (such as sodas, fruit beverages, and fruit juices and nectars) should be limited as much as possible (no more than 1 glass a day).
- Choose products with lower sugar content and reduce the consumption of products with added sugars.
-
Salt in moderate quantity (0.36%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of salt (or sodium) can cause raised blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Many people who have high blood pressure do not know it, as there are often no symptoms.
- Most people consume too much salt (on average 9 to 12 grams per day), around twice the recommended maximum level of intake.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of salt and salted food- Reduce the quantity of salt used when cooking, and don't salt again at the table.
- Limit the consumption of salty snacks and choose products with lower salt content.
-
-
Nutrition facts
Nutrition facts As sold
for 100 g / 100 mlAs sold
per serving (4 biscuits = 67.5 g)Compared to: Biscuits Energy 1,878 kj
(447 kcal)1,270 kj
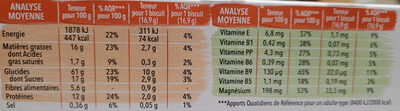
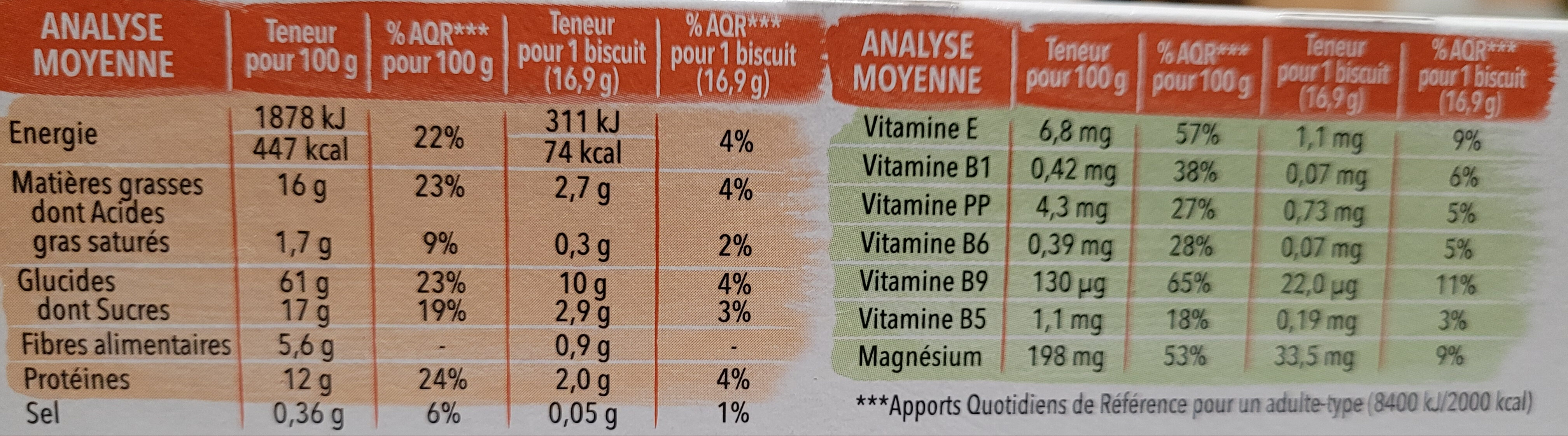
(302 kcal)-4% Fat 16 g 10.8 g -20% Saturated fat 1.7 g 1.15 g -81% Carbohydrates 61 g 41.2 g -5% Sugars 17 g 11.5 g -41% Fiber 5.6 g 3.78 g +96% Proteins 12 g 8.1 g +93% Salt 0.36 g 0.243 g -41% Vitamin E 6.8 mg 4.59 mg +50% Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) 0.42 mg 0.284 mg +62% Vitamin B3/PP (Niacin) 4.3 mg 2.9 mg +10% Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxin) 0.39 mg 0.263 mg +23% Vitamin B9 (Folic acid) 130 µg 87.7 µg +49% Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) 1.1 mg 0.743 mg -40% Magnesium 198 mg 134 mg +286% Fruits‚ vegetables‚ nuts and rapeseed‚ walnut and olive oils (estimate from ingredients list analysis) 20.7 % 20.7 %
Environment
-
Eco-Score C - Moderate environmental impact
⚠ ️Select a country in order to include the full impact of transportation.The Eco-Score is an experimental score that summarizes the environmental impacts of food products.→ The Eco-Score was initially developped for France and it is being extended to other European countries. The Eco-Score formula is subject to change as it is regularly improved to make it more precise and better suited to each country.Life cycle analysis
-
Average impact of products of the same category: B (Score: 69/100)
Category: Biscuit (cookie)
Category: Biscuit (cookie)
- PEF environmental score: 0.35 (the lower the score, the lower the impact)
- including impact on climate change: 2.88 kg CO2 eq/kg of product
Stage Impact Agriculture
80.5 %Processing
11.8 %Packaging
3.1 %Transportation
3.2 %Distribution
1.4 %Consumption
0.0 %
Bonuses and maluses
-
Origins of ingredients with a medium impact
Bonus: +4
Environmental policy: +4
Transportation: 0
Origin of the product and/or its ingredients % of ingredients Impact France 100 %Medium
-
Packaging with a high impact
Malus: -15
Shape Material Recycling Impact Film Unknown High Container Unknown High Bag Unknown High ⚠ ️ The information about the packaging of this product is not sufficiently precise (exact shapes and materials of all components of the packaging).⚠ ️ For a more precise calculation of the Eco-Score, you can modify the product page and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.
Eco-Score for this product
-
Impact for this product: C (Score: 58/100)
Product: Gerble - Soya Fig Cookie, 270g (9.6oz) - 270 g
Life cycle analysis score: 69
Sum of bonuses and maluses: -11
Final score: 58/100
-
Carbon footprint
-
Equal to driving 1.5 km in a petrol car
288 g CO² per 100g of product
The carbon emission figure comes from ADEME's Agribalyse database, for the category: Biscuit (cookie) (Source: ADEME Agribalyse Database)
Stage Impact Agriculture
82.9 %Processing
7.9 %Packaging
3.8 %Transportation
4.7 %Distribution
0.7 %Consumption
0.0 %
Packaging
-
Packaging with a high impact
-
Packaging parts
Film
Container
Bag
-
Packaging materials
Material % Packaging weight Packaging weight per 100 g of product
-
Transportation
-
Origins of ingredients
Origins of ingredients with a medium impact
Origin of the product and/or its ingredients % of ingredients Impact France 100 %Medium
Report a problem
-
Incomplete or incorrect information?
Category, labels, ingredients, allergens, nutritional information, photos etc.
If the information does not match the information on the packaging, please complete or correct it. Open Food Facts is a collaborative database, and every contribution is useful for all.
Data sources
Product added on by ouran
Last edit of product page on by roboto-app.
Product page also edited by alexfauquette, benoitge, countrybot, dan69, date-limite-app, driveoff, ecoscore-impact-estimator, foodvisor, fpdsurveys, gpaum, inf, jaydie, kiliweb, laurence-m-1, magasins-u, manu1400, marilyn, nikezeubi, nparme, openfoodfacts-contributors, packbot, sachab, scanbot, silbon, smoothie-app, thaialagata, tofifi, yuka.RnBveUZyc2RnZDVXa2ZFMTF4WFkxK3d1bm8ycWNHNlJML0FOSWc9PQ, yuka.VjZ0YUNLMEJuTUFnaGRnem93LzAvK3hPbktHakRVYTZJZE16SVE9PQ, yuka.WEljdkg1NWZxNmdMcWM4NnBoSFY2TjlrNXJtTkF6aVFMOHBOSUE9PQ, yuka.YUlVZE5iNExoZjg0c2ZZajh3R0pwZmgxMzRHU1VXU1NlL0VPSVE9PQ, yuka.YUpnQ1MvMEhqS0FYd3RnUnpnUFQyYzVmenAzNWIwU01LL01YSVE9PQ, yuka.YXIwSENZUVJsK3RTaXNBOTl6N002TkZTd0lPb1FGUHVBTThVSVE9PQ.