Help us make food transparency the norm!
As a non-profit organization, we depend on your donations to continue informing consumers around the world about what they eat.
The food revolution starts with you!
Pâte brisée prête à dérouler - Bistro vite - 230 g
Pâte brisée prête à dérouler - Bistro vite - 230 g
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barcode: 3567500070201 (EAN / EAN-13)
Common name: Pâte brisée
Quantity: 230 g
Packaging: Plastic, Protective gas, fr:Papier sulfurisé
Brands: Bistro vite, Vite bon !
Categories: Plant-based foods and beverages, Plant-based foods, Cereals and potatoes, Cereals and their products, Pie dough, Shortcrust pastry
Labels, certifications, awards: Vegetarian, Vegan
Origin of ingredients: France
Traceability code: EMB 67205 - Hœrdt (Bas-Rhin, France)
Stores: Auchan
Countries where sold: France
Matching with your preferences
Health
Ingredients
-
11 ingredients
wheat flour, water, non-hydrogenated vegetable oils and fats, sugar, alcohol, salt, concentrated lemon juice, flour processing agent: l-cysteine, dye: beta-caroteneAllergens: GlutenTraces: Milk
Food processing
-
Ultra processed foods
Elements that indicate the product is in the 4 - Ultra processed food and drink products group:
- Additive: E160a - Carotene
- Ingredient: Colour
Food products are classified into 4 groups according to their degree of processing:
- Unprocessed or minimally processed foods
- Processed culinary ingredients
- Processed foods
- Ultra processed foods
The determination of the group is based on the category of the product and on the ingredients it contains.
Additives
-
E160a - Carotene
Carotene: The term carotene -also carotin, from the Latin carota, "carrot"- is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals -with the exception of some aphids and spider mites which acquired the synthesizing genes from fungi-. Carotenes are photosynthetic pigments important for photosynthesis. Carotenes contain no oxygen atoms. They absorb ultraviolet, violet, and blue light and scatter orange or red light, and -in low concentrations- yellow light. Carotenes are responsible for the orange colour of the carrot, for which this class of chemicals is named, and for the colours of many other fruits, vegetables and fungi -for example, sweet potatoes, chanterelle and orange cantaloupe melon-. Carotenes are also responsible for the orange -but not all of the yellow- colours in dry foliage. They also -in lower concentrations- impart the yellow coloration to milk-fat and butter. Omnivorous animal species which are relatively poor converters of coloured dietary carotenoids to colourless retinoids have yellowed-coloured body fat, as a result of the carotenoid retention from the vegetable portion of their diet. The typical yellow-coloured fat of humans and chickens is a result of fat storage of carotenes from their diets. Carotenes contribute to photosynthesis by transmitting the light energy they absorb to chlorophyll. They also protect plant tissues by helping to absorb the energy from singlet oxygen, an excited form of the oxygen molecule O2 which is formed during photosynthesis. β-Carotene is composed of two retinyl groups, and is broken down in the mucosa of the human small intestine by β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase to retinal, a form of vitamin A. β-Carotene can be stored in the liver and body fat and converted to retinal as needed, thus making it a form of vitamin A for humans and some other mammals. The carotenes α-carotene and γ-carotene, due to their single retinyl group -β-ionone ring-, also have some vitamin A activity -though less than β-carotene-, as does the xanthophyll carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin. All other carotenoids, including lycopene, have no beta-ring and thus no vitamin A activity -although they may have antioxidant activity and thus biological activity in other ways-. Animal species differ greatly in their ability to convert retinyl -beta-ionone- containing carotenoids to retinals. Carnivores in general are poor converters of dietary ionone-containing carotenoids. Pure carnivores such as ferrets lack β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase and cannot convert any carotenoids to retinals at all -resulting in carotenes not being a form of vitamin A for this species-; while cats can convert a trace of β-carotene to retinol, although the amount is totally insufficient for meeting their daily retinol needs.Source: Wikipedia
-
E160ai - Beta-carotene
Beta-Carotene: β-Carotene is an organic, strongly colored red-orange pigment abundant in plants and fruits. It is a member of the carotenes, which are terpenoids -isoprenoids-, synthesized biochemically from eight isoprene units and thus having 40 carbons. Among the carotenes, β-carotene is distinguished by having beta-rings at both ends of the molecule. β-Carotene is biosynthesized from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate.β-Carotene is the most common form of carotene in plants. When used as a food coloring, it has the E number E160a. The structure was deduced by Karrer et al. in 1930. In nature, β-carotene is a precursor -inactive form- to vitamin A via the action of beta-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase.Isolation of β-carotene from fruits abundant in carotenoids is commonly done using column chromatography. It can also be extracted from the beta-carotene rich algae, Dunaliella salina. The separation of β-carotene from the mixture of other carotenoids is based on the polarity of a compound. β-Carotene is a non-polar compound, so it is separated with a non-polar solvent such as hexane. Being highly conjugated, it is deeply colored, and as a hydrocarbon lacking functional groups, it is very lipophilic.Source: Wikipedia
-
E920 - L-cysteine
Cysteine: Cysteine -symbol Cys or C; - is a semi-essential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula HO2CCH-NH2-CH2SH. The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions, as a nucleophile. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. It is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. Cysteine has the same structure as serine, but with one of its oxygen atoms replaced by sulfur; replacing it with selenium gives selenocysteine. -Like other natural proteinogenic amino acids cysteine has -L- chirality in the older D/L notation based on homology to D and L glyceraldehyde. In the newer R/S system of designating chirality, based on the atomic numbers of atoms near the asymmetric carbon, cysteine -and selenocysteine- have R chirality, because of the presence of sulfur -resp. selenium- as a second neighbor to the asymmetric carbon. The remaining chiral amino acids, having lighter atoms in that position, have S chirality.-Source: Wikipedia
Ingredients analysis
-
May contain palm oil
Ingredients that may contain palm oil: Non-hydrogenated vegetable fats, E160ai
-
Vegan
No non-vegan ingredients
-
Vegetarian
No non-vegetarian ingredients detected
-
Details of the analysis of the ingredients
: Farine de blé, eau, huiles et graisses végétales non hydrogénées, sucre, alcool, sel, jus de citron concentré, agent de traitement de la farine (L-cystéine), colorant (béta-carotène)- Farine de blé -> en:wheat-flour - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9410 - percent_min: 11.1111111111111 - percent_max: 100
- eau -> en:water - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 18066 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 50
- huiles et graisses végétales non hydrogénées -> en:non-hydrogenated-vegetable-fats - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - from_palm_oil: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 33.3333333333333
- sucre -> en:sugar - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 31016 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 2.3
- alcool -> en:alcohol - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 1014 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 2.3
- sel -> en:salt - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 11058 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.025
- jus de citron concentré -> en:concentrated-lemon-juice - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 2028 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.025
- agent de traitement de la farine -> en:flour-treatment-agent - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.025
- L-cystéine -> en:e920 - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.025
- colorant -> en:colour - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.025
- béta-carotène -> en:e160ai - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - from_palm_oil: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.025
Nutrition
-
Poor nutritional quality
⚠ ️Warning: the amount of fruits, vegetables and nuts is not specified on the label, it was estimated from the list of ingredients: 0This product is not considered a beverage for the calculation of the Nutri-Score.
Positive points: 1
- Proteins: 4 / 5 (value: 7, rounded value: 7)
- Fiber: 1 / 5 (value: 1.8, rounded value: 1.8)
- Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and colza/walnut/olive oils: 0 / 5 (value: 0.5125, rounded value: 0.5)
Negative points: 14
- Energy: 4 / 10 (value: 1502, rounded value: 1502)
- Sugars: 0 / 10 (value: 2.3, rounded value: 2.3)
- Saturated fat: 6 / 10 (value: 6.5, rounded value: 6.5)
- Sodium: 4 / 10 (value: 410, rounded value: 410)
The points for proteins are not counted because the negative points are greater or equal to 11.
Nutritional score: (14 - 1)
Nutri-Score:
-
Nutrient levels
-
Fat in moderate quantity (14.6%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Saturated fat in high quantity (6.5%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Sugars in low quantity (2.3%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of sugar can cause weight gain and tooth decay. It also augments the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardio-vascular diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of sugar and sugary drinks- Sugary drinks (such as sodas, fruit beverages, and fruit juices and nectars) should be limited as much as possible (no more than 1 glass a day).
- Choose products with lower sugar content and reduce the consumption of products with added sugars.
-
Salt in moderate quantity (1.02%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of salt (or sodium) can cause raised blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Many people who have high blood pressure do not know it, as there are often no symptoms.
- Most people consume too much salt (on average 9 to 12 grams per day), around twice the recommended maximum level of intake.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of salt and salted food- Reduce the quantity of salt used when cooking, and don't salt again at the table.
- Limit the consumption of salty snacks and choose products with lower salt content.
-
-
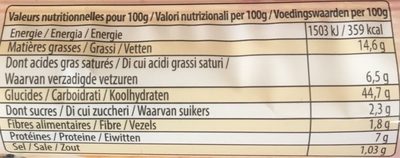
Nutrition facts
Nutrition facts As sold
for 100 g / 100 mlCompared to: Shortcrust pastry Energy 1,502 kj
(359 kcal)-5% Fat 14.6 g -25% Saturated fat 6.5 g -35% Carbohydrates 44.7 g +5% Sugars 2.3 g +1% Fiber 1.8 g -4% Proteins 7 g +17% Salt 1.025 g +3% Fruits‚ vegetables‚ nuts and rapeseed‚ walnut and olive oils (estimate from ingredients list analysis) 0.512 %
Environment
-
Eco-Score C - Moderate environmental impact
⚠ ️Select a country in order to include the full impact of transportation.The Eco-Score is an experimental score that summarizes the environmental impacts of food products.→ The Eco-Score was initially developped for France and it is being extended to other European countries. The Eco-Score formula is subject to change as it is regularly improved to make it more precise and better suited to each country.Life cycle analysis
-
Average impact of products of the same category: B (Score: 66/100)
Category: Short crust pastry, raw
Category: Short crust pastry, raw
- PEF environmental score: 0.37 (the lower the score, the lower the impact)
- including impact on climate change: 3.31 kg CO2 eq/kg of product
Stage Impact Agriculture
67.7 %Processing
10.3 %Packaging
6.1 %Transportation
4.4 %Distribution
2.4 %Consumption
9.2 %
Bonuses and maluses
-
Origins of ingredients with a medium impact
Bonus: +4
Environmental policy: +4
Transportation: 0
Origin of the product and/or its ingredients % of ingredients Impact France 100 %Medium
-
Packaging with a medium impact
Malus: -11
Shape Material Recycling Impact Unknown Paper Low Unknown Plastic High ⚠ ️ The information about the packaging of this product is not sufficiently precise (exact shapes and materials of all components of the packaging).⚠ ️ For a more precise calculation of the Eco-Score, you can modify the product page and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.
Eco-Score for this product
-
Impact for this product: C (Score: 59/100)
Product: Pâte brisée prête à dérouler - Bistro vite - 230 g
Life cycle analysis score: 66
Sum of bonuses and maluses: -7
Final score: 59/100
-
Carbon footprint
-
Equal to driving 1.7 km in a petrol car
331 g CO² per 100g of product
The carbon emission figure comes from ADEME's Agribalyse database, for the category: Short crust pastry, raw (Source: ADEME Agribalyse Database)
Stage Impact Agriculture
76.2 %Processing
5.5 %Packaging
8.2 %Transportation
6.2 %Distribution
1.1 %Consumption
2.8 %
Packaging
-
Packaging with a medium impact
-
Packaging parts
(Paper)
(Plastic)
-
Packaging materials
Material % Packaging weight Packaging weight per 100 g of product Paper or cardboard Plastic Total
-
Transportation
-
Origins of ingredients
Origins of ingredients with a medium impact
Origin of the product and/or its ingredients % of ingredients Impact France 100 %Medium
Report a problem
-
Incomplete or incorrect information?
Category, labels, ingredients, allergens, nutritional information, photos etc.
If the information does not match the information on the packaging, please complete or correct it. Open Food Facts is a collaborative database, and every contribution is useful for all.
Data sources
Product added on by jeanbono
Last edit of product page on by packbot.
Product page also edited by desan, inf, kiliweb, openfoodfacts-contributors, teolemon, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlkhhXIfi-yiZCgTlhU6Hwu2ND5nDW9pPv6faNKs.