Help us make food transparency the norm!
As a non-profit organization, we depend on your donations to continue informing consumers around the world about what they eat.
The food revolution starts with you!
Noir noisettes sans sucre ajoutés - Villars - 100 g
Noir noisettes sans sucre ajoutés - Villars - 100 g
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barcode: 7610036002669 (EAN / EAN-13)
Quantity: 100 g
Packaging: Cardboard
Brands: Villars
Categories: Snacks, Sweet snacks, Cocoa and its products, Chocolates, Chocolates with sweeteners, Dark chocolates, Dark chocolates with sweeteners
Labels, certifications, awards: Low or no sugar, No added sugar
Manufacturing or processing places: Suisse
Countries where sold: France
Matching with your preferences
Health
Ingredients
-
12 ingredients
: pâte de cacao, édulcorant : isomalt, beurre de cacao, éclats de noisettes (10 %), gomme d'acacia (fibre), émulsifiant : lécithine de soja, arôme naturel de vanille, édulcorant : glycoside de stéviol.Allergens: Nuts, SoybeansTraces: Eggs, Gluten, Milk, Nuts
Food processing
-
Ultra processed foods
Elements that indicate the product is in the 4 - Ultra processed food and drink products group:
- Additive: E322 - Lecithins
- Additive: E414 - Acacia gum
- Additive: E953 - Isomalt
- Additive: E960 - Steviol glycosides
- Ingredient: Emulsifier
- Ingredient: Flavouring
- Ingredient: Sweetener
Food products are classified into 4 groups according to their degree of processing:
- Unprocessed or minimally processed foods
- Processed culinary ingredients
- Processed foods
- Ultra processed foods
The determination of the group is based on the category of the product and on the ingredients it contains.
Additives
-
E322 - Lecithins
Lecithins are natural compounds commonly used in the food industry as emulsifiers and stabilizers.
Extracted from sources like soybeans and eggs, lecithins consist of phospholipids that enhance the mixing of oil and water, ensuring smooth textures in various products like chocolates, dressings, and baked goods.
They do not present any known health risks.
-
E322i - Lecithin
Lecithins are natural compounds commonly used in the food industry as emulsifiers and stabilizers.
Extracted from sources like soybeans and eggs, lecithins consist of phospholipids that enhance the mixing of oil and water, ensuring smooth textures in various products like chocolates, dressings, and baked goods.
They do not present any known health risks.
-
E414 - Acacia gum
Gum arabic: Gum arabic, also known as acacia gum, arabic gum, gum acacia, acacia, Senegal gum and Indian gum, and by other names, is a natural gum consisting of the hardened sap of various species of the acacia tree. Originally, gum arabic was collected from Acacia nilotica which was called the "gum arabic tree"; in the present day, gum arabic is collected from acacia species, predominantly Acacia senegal and Vachellia -Acacia- seyal; the term "gum arabic" does not indicate a particular botanical source. In a few cases so‐called "gum arabic" may not even have been collected from Acacia species, but may originate from Combretum, Albizia or some other genus. Producers harvest the gum commercially from wild trees, mostly in Sudan -80%- and throughout the Sahel, from Senegal to Somalia—though it is historically cultivated in Arabia and West Asia. Gum arabic is a complex mixture of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. It is the original source of the sugars arabinose and ribose, both of which were first discovered and isolated from it, and are named after it. Gum arabic is soluble in water. It is edible, and used primarily in the food industry as a stabilizer, with EU E number E414. Gum arabic is a key ingredient in traditional lithography and is used in printing, paint production, glue, cosmetics and various industrial applications, including viscosity control in inks and in textile industries, though less expensive materials compete with it for many of these roles. While gum arabic is now produced throughout the African Sahel, it is still harvested and used in the Middle East.Source: Wikipedia
-
E953 - Isomalt
Isomalt: Isomalt is a sugar substitute, a type of sugar alcohol used primarily for its sugar-like physical properties. It has little to no impact on blood sugar levels, and does not stimulate the release of insulin. It also does not promote tooth decay, i.e. is tooth-friendly. Its energy value is 2 kcal/g, half that of sugars. However, like most sugar alcohols, it carries a risk of gastric distress, including flatulence and diarrhea, when consumed in large quantities -above about 20-30 g per day-. Isomalt may prove upsetting to the intestinal tract because it is incompletely absorbed in the small intestine, and when polyols pass into the large intestine, they can cause osmotically induced diarrhea and stimulate the gut flora, causing flatulence. As with other dietary fibers, regular consumption of isomalt can lead to desensitisation, decreasing the risk of intestinal upset. Isomalt can be blended with high-intensity sweeteners such as sucralose, giving a mixture that has the same sweetness as sugar. Isomalt is an equimolar mixture of two mutually diastereomeric disaccharides, each composed of two sugars: glucose and mannitol -α-D-glucopyranosido-1‚6-mannitol- and also glucose and sorbitol -α-D-glucopyranosido-1‚6-sorbitol-. Complete hydrolysis of isomalt yields glucose -50%-, sorbitol -25%-, and mannitol -25%-. It is an odorless, white, crystalline substance containing about 5% water of crystallisation. Isomalt has a minimal cooling effect -positive heat of solution-, lower than many other sugar alcohols, in particular, xylitol and erythritol. Isomalt is manufactured in a two-stage process in which sucrose is first transformed into isomaltulose, a reducing disaccharide -6-O-α-D-glucopyranosido-D-fructose-. The isomaltulose is then hydrogenated, using a Raney nickel catalyst. The final product — isomalt — is an equimolar composition of 6-O-α-D-glucopyranosido-D-sorbitol -1‚6-GPS- and 1-O-α-D-glucopyranosido-D-mannitol-dihydrate -1‚1-GPM-dihydrate-. Isomalt has been approved for use in the United States since 1990. It is also permitted for use in Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Mexico, Iran, the European Union, and other countries. Isomalt is widely used for the production of sugar-free candy, especially hard-boiled candy, because it resists crystallisation much better than the standard combinations of sucrose and corn syrup. It is used in sugar sculpture for the same reason.Source: Wikipedia
-
E960 - Steviol glycosides
Steviol glycoside: Steviol glycosides are the chemical compounds responsible for the sweet taste of the leaves of the South American plant Stevia rebaudiana -Asteraceae- and the main ingredients -or precursors- of many sweeteners marketed under the generic name stevia and several trade names. They also occur in the related species Stevia phlebophylla -but in no other species of Stevia- and in the plant Rubus chingii -Rosaceae-.Steviol glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana have been reported to be between 30 and 320 times sweeter than sucrose, although there is some disagreement in the technical literature about these numbers. They are heat-stable, pH-stable, and do not ferment. Additionally, they do not induce a glycemic response when ingested, because humans can not metabolize stevia. This makes them attractive as natural sugar substitutes for diabetics and other people on carbohydrate-controlled diets. Steviol glycosides stimulate the insulin secretion through potentiation of the β-cell, preventing high blood glucose after a meal. The acceptable daily intake -ADI- for steviol glycosides, expressed as steviol equivalents, has been established to be 4 mg/kg body weight/day, and is based on no observed effects of a 100 fold higher dose in a rat study.Source: Wikipedia
Ingredients analysis
-
Palm oil free
No ingredients containing palm oil detected
-
Vegan status unknown
Unrecognized ingredients: Fiber
-
Vegetarian status unknown
Unrecognized ingredients: Fiber
-
Details of the analysis of the ingredients
: pâte de cacao, édulcorant (isomalt), beurre de cacao, éclats de _noisettes_ 10%, gomme d'acacia (fibre), émulsifiant (lécithine de _soja_), arôme naturel de vanille, édulcorant (glycoside de stéviol)- pâte de cacao -> en:cocoa-paste - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 16030 - percent_min: 12.5 - percent_max: 70
- édulcorant -> en:sweetener - percent_min: 10 - percent_max: 40
- isomalt -> en:e953 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 10 - percent_max: 40
- beurre de cacao -> en:cocoa-butter - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 16030 - percent_min: 10 - percent_max: 30
- éclats de _noisettes_ -> fr:eclats-de-noisettes - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 15004 - percent_min: 10 - percent: 10 - percent_max: 10
- gomme d'acacia -> en:e414 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 10
- fibre -> en:fiber - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 10
- émulsifiant -> en:emulsifier - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 10
- lécithine de _soja_ -> en:soya-lecithin - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 42200 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 10
- arôme naturel de vanille -> en:natural-vanilla-flavouring - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- édulcorant -> en:sweetener - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- glycoside de stéviol -> en:e960 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
Nutrition
-
Poor nutritional quality
⚠ ️Warning: the amount of fruits, vegetables and nuts is not specified on the label, it was estimated from the list of ingredients: 10This product is not considered a beverage for the calculation of the Nutri-Score.
Positive points: 5
- Proteins: 4 / 5 (value: 6.5, rounded value: 6.5)
- Fiber: 5 / 5 (value: 15, rounded value: 15)
- Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and colza/walnut/olive oils: 0 / 5 (value: 10, rounded value: 10)
Negative points: 16
- Energy: 6 / 10 (value: 2180, rounded value: 2180)
- Sugars: 0 / 10 (value: 0.5, rounded value: 0.5)
- Saturated fat: 10 / 10 (value: 25, rounded value: 25)
- Sodium: 0 / 10 (value: 36, rounded value: 36)
The points for proteins are not counted because the negative points are greater or equal to 11.
Nutritional score: (16 - 5)
Nutri-Score:
-
Nutrient levels
-
Fat in high quantity (46%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Saturated fat in high quantity (25%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Sugars in low quantity (0.5%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of sugar can cause weight gain and tooth decay. It also augments the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardio-vascular diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of sugar and sugary drinks- Sugary drinks (such as sodas, fruit beverages, and fruit juices and nectars) should be limited as much as possible (no more than 1 glass a day).
- Choose products with lower sugar content and reduce the consumption of products with added sugars.
-
Salt in low quantity (0.09%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of salt (or sodium) can cause raised blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Many people who have high blood pressure do not know it, as there are often no symptoms.
- Most people consume too much salt (on average 9 to 12 grams per day), around twice the recommended maximum level of intake.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of salt and salted food- Reduce the quantity of salt used when cooking, and don't salt again at the table.
- Limit the consumption of salty snacks and choose products with lower salt content.
-
-
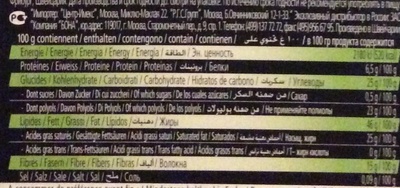
Nutrition facts
Nutrition facts As sold
for 100 g / 100 mlCompared to: Dark chocolates with sweeteners Energy 2,180 kj
(521 kcal)+6% Fat 46 g +22% Saturated fat 25 g +11% Trans fat 0 g Carbohydrates 25 g -33% Sugars 0.5 g -52% Polyols (sugar alcohols) 23 g -27% Fiber 15 g +26% Proteins 6.5 g -11% Salt 0.09 g +71% Fruits‚ vegetables‚ nuts and rapeseed‚ walnut and olive oils (estimate from ingredients list analysis) 10 % Cocoa (minimum) 70 % +12%
Environment
-
Eco-Score D - High environmental impact
⚠ ️Select a country in order to include the full impact of transportation.The Eco-Score is an experimental score that summarizes the environmental impacts of food products.→ The Eco-Score was initially developped for France and it is being extended to other European countries. The Eco-Score formula is subject to change as it is regularly improved to make it more precise and better suited to each country.Life cycle analysis
-
Average impact of products of the same category: D (Score: 35/100)
Category: Dark chocolate bar, without sugar and with artificial sweeteners
Category: Dark chocolate bar, without sugar and with artificial sweeteners
- PEF environmental score: 0.89 (the lower the score, the lower the impact)
- including impact on climate change: 17.11 kg CO2 eq/kg of product
Stage Impact Agriculture
14.3 %Processing
81.0 %Packaging
1.2 %Transportation
3.0 %Distribution
0.5 %Consumption
0.0 %
Bonuses and maluses
-
Missing origins of ingredients information
Malus: -5
⚠ ️ The origins of the ingredients of this product are not indicated.
If they are indicated on the packaging, you can modify the product sheet and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.
-
Packaging with a low impact
Malus: -1
Shape Material Recycling Impact Unknown Cardboard Low ⚠ ️ The information about the packaging of this product is not sufficiently precise (exact shapes and materials of all components of the packaging).⚠ ️ For a more precise calculation of the Eco-Score, you can modify the product page and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.
Eco-Score for this product
-
Impact for this product: D (Score: 29/100)
Product: Noir noisettes sans sucre ajoutés - Villars - 100 g
Life cycle analysis score: 35
Sum of bonuses and maluses: -6
Final score: 29/100
-
Carbon footprint
-
Equal to driving 8.9 km in a petrol car
1711 g CO² per 100g of product
The carbon emission figure comes from ADEME's Agribalyse database, for the category: Dark chocolate bar, without sugar and with artificial sweeteners (Source: ADEME Agribalyse Database)
Stage Impact Agriculture
8.6 %Processing
89.2 %Packaging
0.6 %Transportation
1.6 %Distribution
0.1 %Consumption
0.0 %
Packaging
-
Packaging with a low impact
-
Packaging parts
(Cardboard)
-
Packaging materials
Material % Packaging weight Packaging weight per 100 g of product Paper or cardboard
-
Transportation
-
Origins of ingredients
Missing origins of ingredients information
⚠ ️ The origins of the ingredients of this product are not indicated.
If they are indicated on the packaging, you can modify the product sheet and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.Add the origins of ingredients for this product Add the origins of ingredients for this product
Report a problem
-
Incomplete or incorrect information?
Category, labels, ingredients, allergens, nutritional information, photos etc.
If the information does not match the information on the packaging, please complete or correct it. Open Food Facts is a collaborative database, and every contribution is useful for all.
Data sources
Product added on by openfoodfacts-contributors
Last edit of product page on by packbot.
Product page also edited by elttor, tacite, tacite-mass-editor, teolemon.